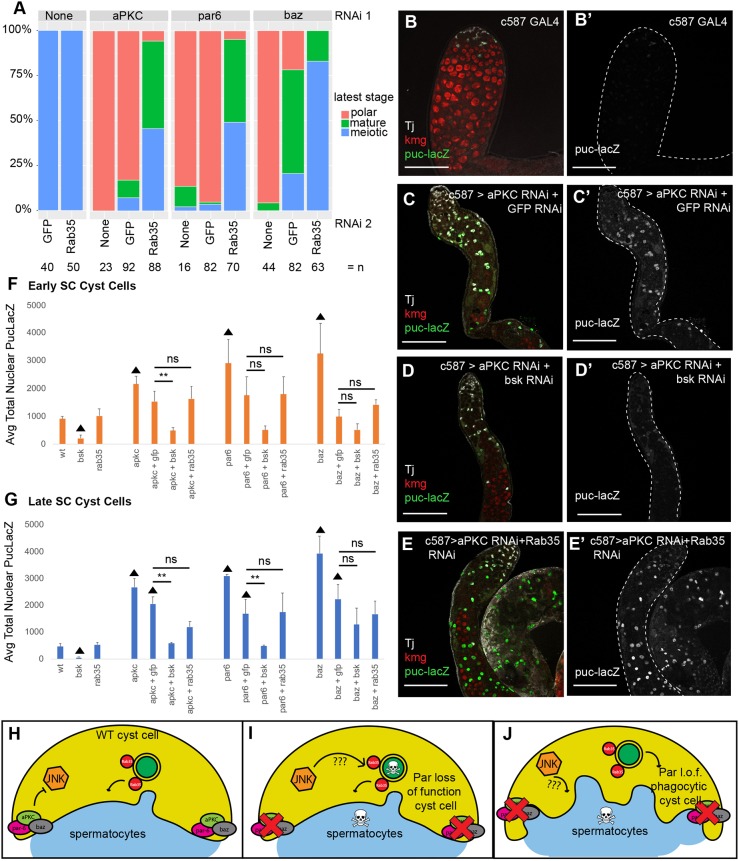
Fig. 7.
Rab35 acts downstream or in parallel to the JNK pathway in cyst cells following Par complex loss of function to cause spermatocyte death. (A) Quantification of phenotype distribution for testes of the indicated genotypes 8 days after a shift to 30°C. P<10−12 by Fisher's exact test compared with double RNAi control. (B-E′) Immunofluorescence images of testes from flies expressing Puc-LacZ (green, B-E; gray, B′-E′) shifted to 30°C for 8 days after eclosion and stained using anti-βgal (green), anti-Tj (gray, cyst cell nuclei) and anti-Kmg (red, spermatocyte nuclei) antibodies. Scale bars: 50 μm. (F,G) Quantification of nuclear Puc-LacZ fluorescence intensity in (F) early and (G) late spermatocyte-associated cyst cells (SC CCs). n>25 cells from each of at least two biological replicates. Significance was determined using Student's one-tailed t-test (**P<0.05; ▴ indicates P<0.05 compared with wild type). (H) The Par complex represses JNK pathway activation in wild-type cyst cells. (I,J) Loss of function of the Par complex in cyst cells results in spermatocyte death by activation of the JNK pathway (I), which may deliver a pro-death or pro-apoptotic signal to the germ line via Rab35. (J) Rab35 may also work in parallel to the JNK signaling pathway in Par loss-of-function cyst cells to induce spermatocyte phagocytosis by the cyst cells.