Fig. 2.
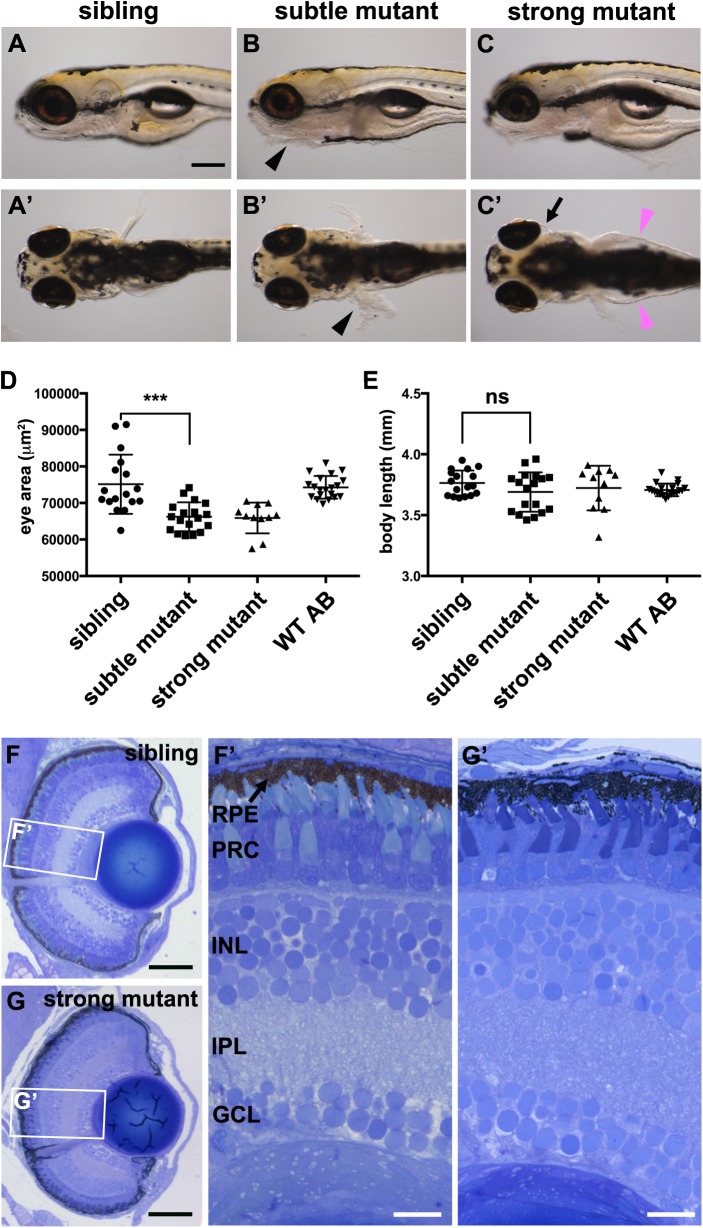
pen/lgl2 larvae have smaller but morphologically normal eyes at 5 dpf. (A–C′) pen/lgl2 eye phenotype at 5 dpf. Panels show examples of sibling (A,A′), subtle mutant (B,B′) and strong mutant (C,C′) phenotypes. Mutants were scored based on skin phenotype (B,B′, black arrowheads). pen/lgl2 mutants with strong phenotype display severe edema (C′, magenta arrowheads) and detachment of the eyes (C′, arrow). Scale bar: 250 µm. (D,E) Measurements of lateral eye surface area (D) and body length (E) at 5 dpf in WT (n=20), pen/lgl2 sibling (n=17), subtle (n=18) and strong (n=11) phenotype mutant larvae. pen/lgl2 mutants display a significantly smaller eye size in comparison to sibling larvae. Graphs show mean±s.d. ***P=0.0002; ns, not significant (P=0.1148) by t-test (unpaired, with equal s.d., two-tailed). (F–G′) Toluidine Blue staining of transverse histological sections shows that, in comparison to siblings (F,F′), pen/lgl2 strong mutant retinas laminate normally (G,G′). RPE, retinal pigment epithelium; PRC, photoreceptor cell layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; IPL, inner plexiform layer; GCL, ganglion cell layer. Scale bars: (F,G) 50 µm; (F′,G′) 10 µm.