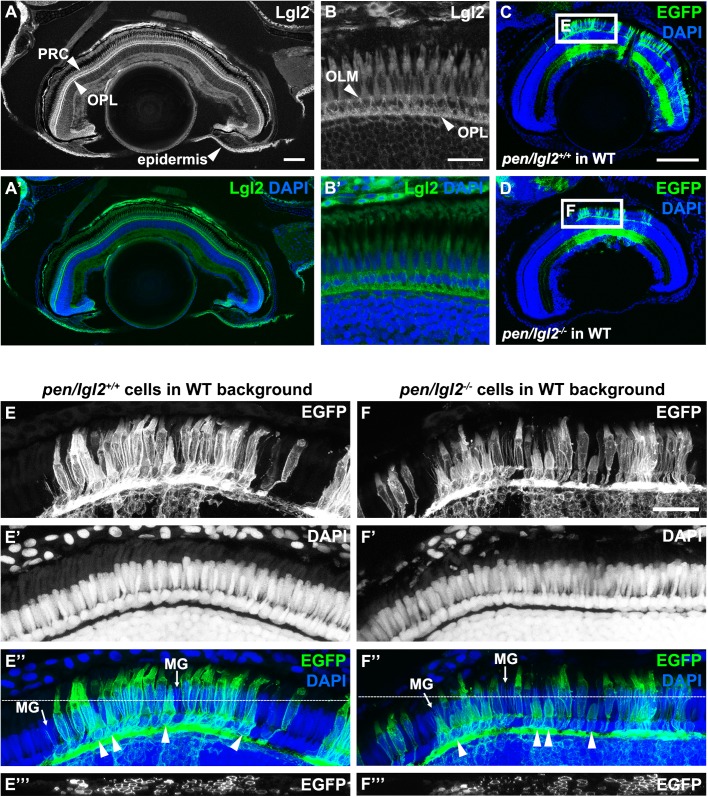
Fig. 4.
Lgl2 expression persists in juvenile fish but endogenous zygotic Lgl2 expression is not required for PRC survival. (A–B′) Lgl2 expression in a juvenile [10.6 mm standard length (SL)] retina. (A,A′) Lgl2 expression is detected in the epidermis and the distal retina of juvenile fish. Scale bar: 100 µm. (B,B′) Lgl2 localizes basolaterally in juvenile photoreceptors. RPE expression could not be analyzed due to pigmentation. Scale bar: 20 µm. PRC, photoreceptor cells; OLM, outer limiting membrane; OPL, outer plexiform layer. (C–F′′′) Immunostaining of transverse retinal sections of juvenile chimeric fish. EGFP-labelled sibling pen/lgl2+/+ (C, 5.5 mm SL) or EGFP-labelled mutant pen/lgl2−/− (D, 5.4 mm SL) cells were transplanted into WT hosts and analyzed at 4 weeks. (C,D) Overview of the eye shows location of the transplanted EGFP+ cells in the retina. Boxed regions are shown in E–F′′′. Scale bar: 100 µm. (E–F′′′) Transplanted WT (E–E′′′) or pen/lgl2 mutant (F–F′′′) cells (marked by EGFP) differentiate into various retinal cell types. Different types of cones can be distinguished by cell size. In E″ and F″, arrowheads denote UV cones and MG labels Müller glia processes. White lines in E″ and F″ mark the level of the orthogonal view shown in panels E′′′ and F′′′. Scale bar: 20 µm.