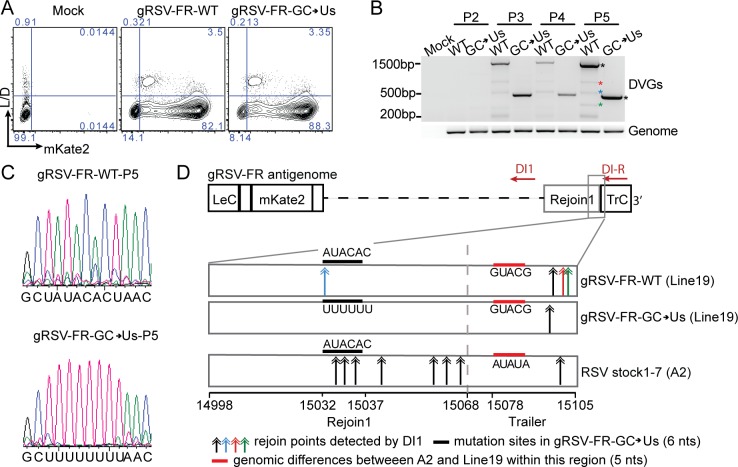
Fig 5. A conserved rejoin region determines cbDVG formation during viral infection in tissue culture.
(A) HEp2 cells were infected with gRSV-FR-WT-P3 and gRSV-FR-GC>Us-P3 at MOI of 1.5 and harvested at 72 h post infection and stained with LIVE/DEAD Aqua, followed by flow cytometry for mKate2 expression as a proxy for virus replication. (B) cbDVG detection from P2, P3, P4, and P5 of gRSV-FR-WT and gRSV-FR-GC>Us via DVG specific RT-PCR using DI1/DI-R primer set in HEp2 cell. Confirmed cbDVG-like fragments are labeled with asterisks next to the gel. Different colors correspond to the color of double arrows in Fig 4D. Sequence of confirmed DVGs are listed in S3G and S3H Fig. (C) Confirmation of introduced mutations in gRSV-FR-GC->Us-P5 infected cells via Sanger sequencing. (D) Schematic summary of all identified cbDVG rejoin points within positions 14998–15105 (RSV A2, reference genome NCBI KT992094.1) generated during infections with gRSV-FR-WT, gRSV-FR-GC>Us, and RSV stocks1-7. All DVGs were detected by DVG specific RT-PCR using the DI1/DI-R primer set. RSV HD stock1-7 are strain A2 and gRSV-FR-WT and gRSV-FR-CG->Us are strain Line19. The sequence difference between A2 and line 19 within common rejoin region is indicated by red thick lines. Colored double arrows indicated the rejoin points of cbDVGs detected from viruses. Black thick lines mark the 6 nucleotides mutated in gRSV-FR-GC->Us.