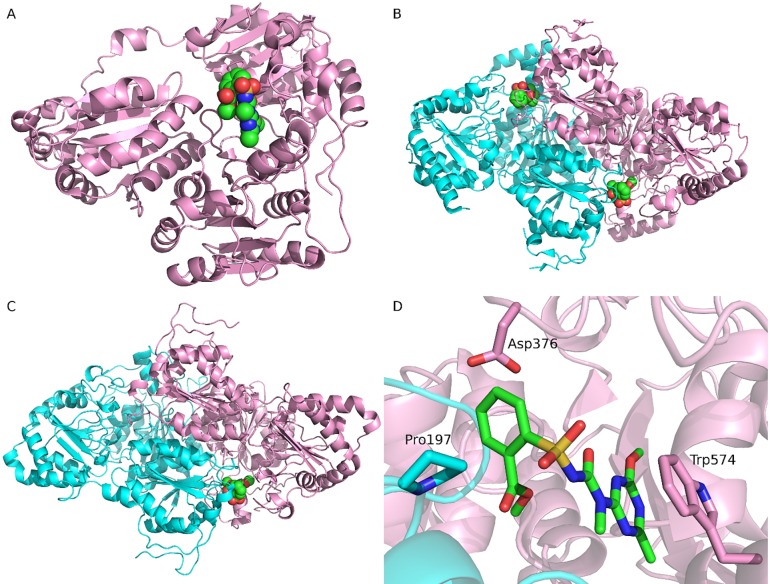
Fig 2. The complex structures of AHAS bound with tribenuron methyl.
(A) The monomer structure of Arabidopsis thaliana AHAS (AtAHAS) bound with tribenuron methyl (1YI1). (B) The dimer structure of Saccharomyces cerevisiae AHAS (ScAHAS) bound with tribenuron methyl (1T9A). (C) The modeled dimer structure of Kochia scoparia AHAS (KsAHAS) bound with tribenuron methyl. (D) Important interactions between ScAHAS and tribenuron methyl (1T9A). In panels A, B, and C, tribenuron methyl is displayed in spheres, indicating the binding site. In panels B, C, and D, the two chains of AHAS are colored pink and cyan, respectively. In panel D, tribenuron methyl and three important residues are shown in sticks. Carbons in tribenuron methyl are colored green.