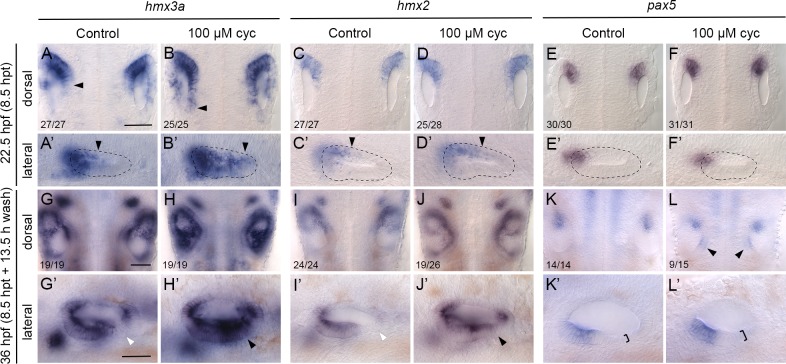
Fig 3. Expression of the otic anterior marker genes hmx3a, hmx2 and pax5 after Hh pathway inhibition.
Expression of mRNA for anterior otic markers in embryos treated with 100 μM cyclopamine (cyc) from the 10-somite stage (14 hpf) until 22.5 hpf. Controls in the left-hand panels of each pair of images were treated with vehicle (ethanol) only. (A–F’) At 22.5 hpf (8.5 hours post initiation of treatment, hpt), expression of hmx3a expanded into posterior regions of the otic vesicle (arrowheads); expression of hmx2 showed a modest expansion and there was no change in the otic expression pattern of pax5. Arrowheads in A–D’ indicate posterior extent of otic expression. (G–L’) At 36 hpf (8.5 hpt + 13.5 h wash), expression of both hmx3a and hmx2 extended into posteroventral regions of the otic epithelium. White arrowheads indicate regions that are normally free of expression in controls; black arrowheads mark ectopic expression in cyclopamine-treated embryos. By 36 hpf, expression of pax5 appeared in a new discrete domain in posteromedial otic epithelium after cyclopamine treatment (L, arrowheads); in a lateral view, the epithelium in posterolateral regions was thicker than normal (K’,L’, brackets). A–L are dorsal views showing both otic vesicles, with anterior to the top; A’–L’ are lateral views with anterior to the left. Scale bars, 50 μm (scale bar in A applies to A–F’; in G applies to G–L; in G’ applies to G’–L’).