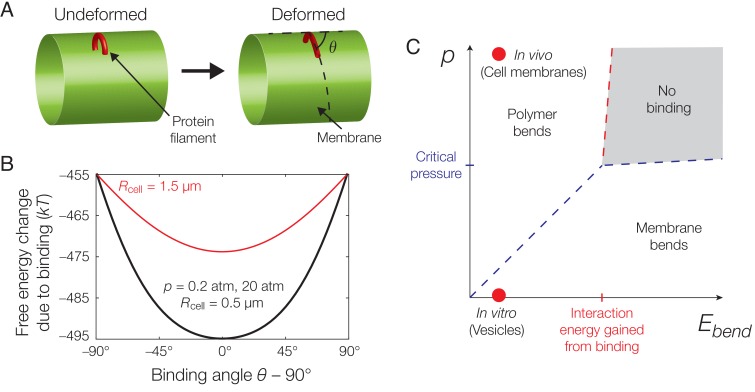
Figure 2. Mechanics of binding.
(A) A schematic of the model. A protein filament (red) may bend and bind to a cylindrical membrane (green) at an angle with respect to the long axis, , and the equilibrium conformation may involve deformations of both protein and membrane. (B) Plot of the estimated free energy change due to filament binding against the binding angle, , where the cell radius , the pressure difference across the membrane , the estimated turgor pressure of B. subtilis (Whatmore and Reed, 1990), and the other model parameters are given in Supplementary file 1. The estimate is similar for , but exhibits a more shallow potential well for (red curve). (C) An approximate phase diagram of protein-membrane binding. The dashed lines delineate regimes, as explained further in Appendix 1.