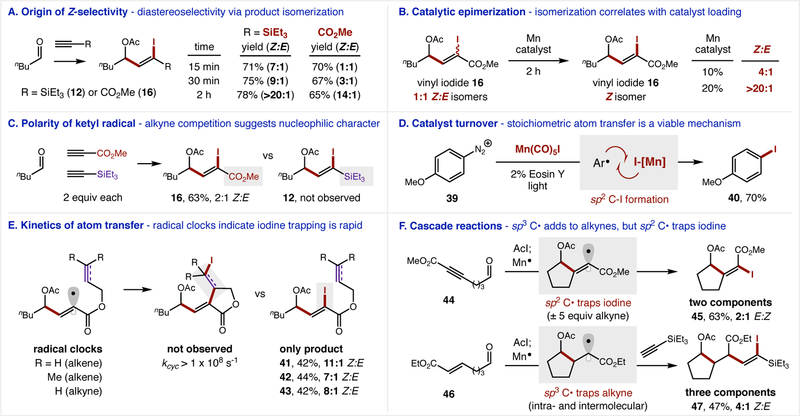
Figure 3. Mechanistic experiments.
(A) Z:E selectivity increases over the reaction course (for both alkyne classes) suggesting a product isomerization pathway. (B) A 1:1 mixture of vinyl iodide isomerizes to increased ratios of the Z-isomer correlating with Mn catalyst loading, illustrating the catalyst’s role in isomerization. (C) Selective combination with an electron-deficient alkyne indicates the ketyl radical is nucleophilic. (D) The catalyst turnover step involving sp2 C-I formation is recapitulated by trapping an aryl radical with [Mn]-I to form Ar-I. (E) Selective recombination of the vinyl radical with I• (vs intramolecular traps) suggests this step is rapid. (F) Intramolecular traps with sp2 or sp3 C• intermediates afford either two- or three-component cascade couplings.