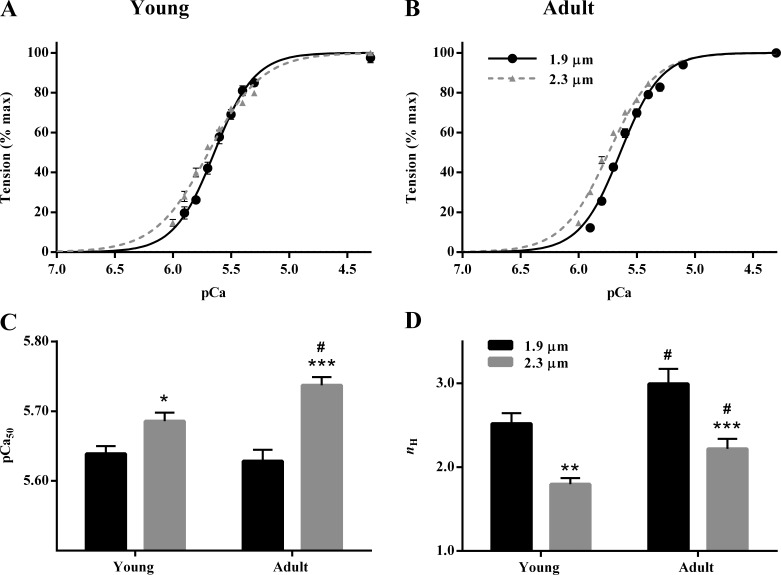
Figure 2.
SL dependency of the pCa–tension relation in young and adult guinea pig cardiac muscle preparations. Normalized steady state tensions at various pCa were plotted against pCa to construct the pCa–tension relationships. The Hill model was fitted to pCa–tension relationships to derive myofilament Ca2+ sensitivity (pCa50) and myofilament cooperativity (nH). (A and B) Comparisons of pCa–tension relationships at short and long SL in young (A) and adult (B) muscle preparations. The traces connecting the experimental data points are the Hill model fits. Error bars are obscured by the symbols in some cases. (C and D) Bar graphs showing the SL-dependent effect on pCa50 (C) and nH (D) in young and adult muscle preparations. Two-way ANOVA revealed a significant SL–MHC interaction effect (P = 0.02) on pCa50. For nH, the main effects of both SL (P < 0.001) and MHC (P = 0.0013) were significant. Post hoc multiple comparisons (Holm–Sidak method) were used to determine significant differences between groups. Asterisks and hash marks indicate significant difference when compared with data within each group (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; and ***, P < 0.001 for 1.9 vs. 2.3 µm; #, P < 0.05 for young vs. adult). The number of preparations measured for all groups was 10. Data are expressed as means ± SEM.