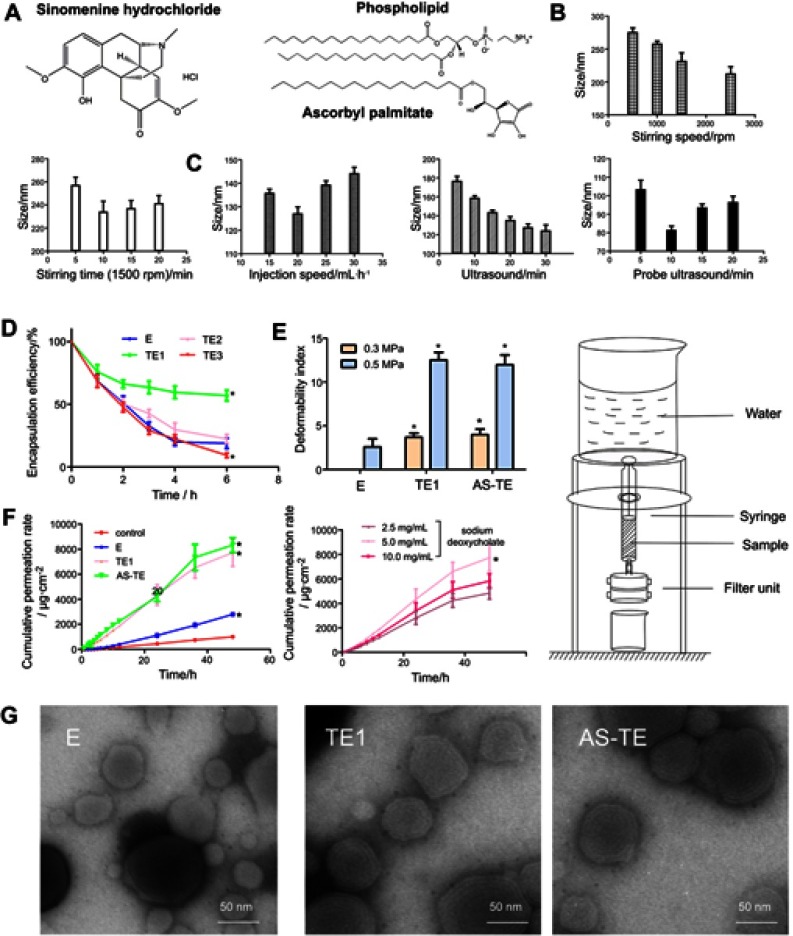
Figure 1.
(A) The chemical structure of sinomenine hydrochloride, phospholipid, and ascorbyl palmitate. (B) The ethosomal sizes were prepared by different stirring velocities and time on the basis of the stirring-injection method. (C) The ethosomal sizes were prepared by different injection velocities, ultrasound time, and probe ultrasound time based on ultrasound-injection method. (D) The capsulation efficiency with different edge activators (*P<0.05 vs E). (E) The deformability indexes under 0.3 and 0.5 MPa were measured by self-made equipment on the right. (*P< 0.05 vs E). (F) The cumulative permeation rates in vitro of control (sinomenine hydrochloride normal saline solution), E, and TE1, containing different concentrations of sodium deoxycholate, and AS-TE. (*P <0.05 vs control and TE1 containing 5.0 mg/mL of sodium deoxycholate). (G) The TEM images of E, TE1, and AS-TE.
Abbreviations: E, ethosome; TE, transethosomes (ethosome containing sodium deoxycholate (TE1), tween-80 (TE2) and oleic acid (TE3)); AS-TE, antioxidant surface transethosome.