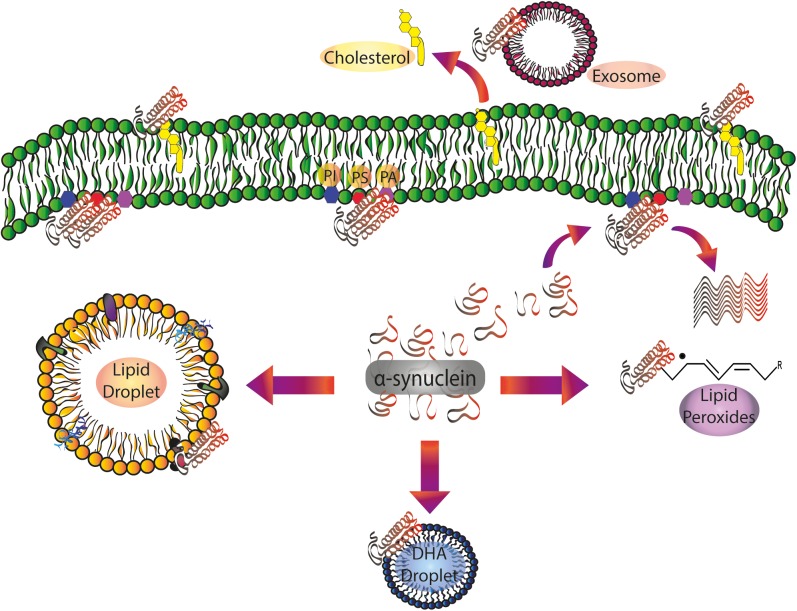
FIGURE 1.
α-Synuclein/lipid interactions: from the plasma membrane to intracellular compartments and extracellular vesicles. Soluble α-synuclein exists as a random coil three-dimensional structure. Membrane targeting with acidic PLs (PS and PI) triggers α-helical folding at the N-terminal domain. Protein pathological conformation is predominantly represented by β-sheet oligomers and amyloid fibrils. α-Synuclein pathological aggregation is dependent on the protein/lipid ratio. Spreading of α-synuclein, largely attributed to exosomes, is also regulated by its interaction with the PLs of the extracellular vesicles. Free fatty acids, mainly DHA, are able to induce α-synuclein oligomerization. After the interaction with lipid peroxidation products, α-synuclein is prone to the formation of toxic stable oligomers. α-Synuclein also regulates Chol efflux via ABCA1 transporter. DHA, docosahexaenoic acid; PA: phosphatidic acid; PI, phosphatidylinositol; PS, phosphatidylserine.