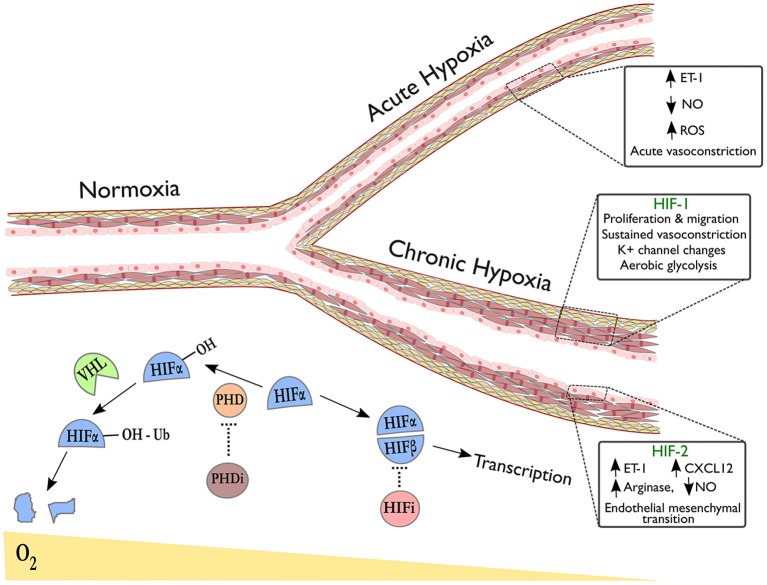
Figure 1.
Pulmonary vascular responses to hypoxia with emphasis on the role of HIF isoforms in remodeling. The right upper branch of this vessel depicts vasoconstriction in acute hypoxia, occurring due to alterations in redox and NO signaling and release of vasoactive mediators. The lower branch indicates remodeling in the context of sustained hypoxic exposure and illustrates HIF-dependent processes revealed by tissue-specific deletion of HIF-isoforms in endothelial cells (HIF-2α) or smooth muscle cells (HIF-1α). Below the vessel, a schematic shows degradation of hydroxylated HIF-α subunits in normoxia via the von-Hippel Lindau (VHL) pathway. In hypoxia or following treatment with prolyl hydroxylase inhibitors (PHDi), HIF-α stabilization and dimerization with HIF-β occurs, leading to transcription of target genes. HIF inhibitors (HIFi) with specific activity against HIF-2α are in clinical development.