Figure 4.
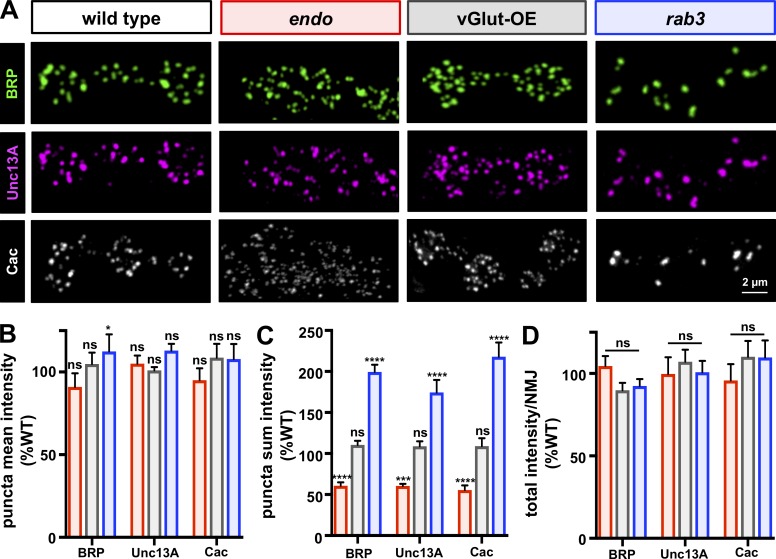
BRP, Unc13A, and Cac abundance scale in endo and rab3 mutants, while total levels per NMJ remain constant. (A) Representative type Ib boutons immunostained with anti-BRP, anti-Unc13A, and endogenously tagged Ca2+ channels (CacsfGFP-N) in the indicated genotypes (wild type: cacsfGFP-N; endo: cacsfGFP-N;endo1/endoΔ4; vGlut-OE: cacsfGFP-N;OK371-Gal4/UAS-vGlut; rab3: cacsfGFP-N;rab3rup). Note that BRP and Unc13A are costained at the same NMJ, while Cac images were acquired from a different NMJ of the same genotype. (B) Quantification of mean fluorescence intensity of individual BRP, Unc13A, and CacsfGFP-N puncta shows no change in endo and vGlut-OE, with a slight but significant increase in rab3, consistent with no major difference in the density of material within each punctum. (C) Quantification of BRP, Unc13A, and CacsfGFP-N puncta sum fluorescence intensity reveals a significant reduction in endo, an increase in rab3, and no change in vGlut-OE, consistent with the observed changes in puncta area for each genotype (n ≥ 15; one-way ANOVA; Table S1). (D) The total fluorescence intensity of each individual BRP, Unc13A, and CacsfGFP-N puncta summed across the entire muscle 4 NMJ terminal is unchanged in endo, rab3, and vGlut-OE compared with wild type. Error bars indicate ± SEM (n ≥ 8; one-way ANOVA; Table S1). *, P < 0.05; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001; ns, not significant. See Materials and methods for more details on mean, sum, and total intensity measurements.