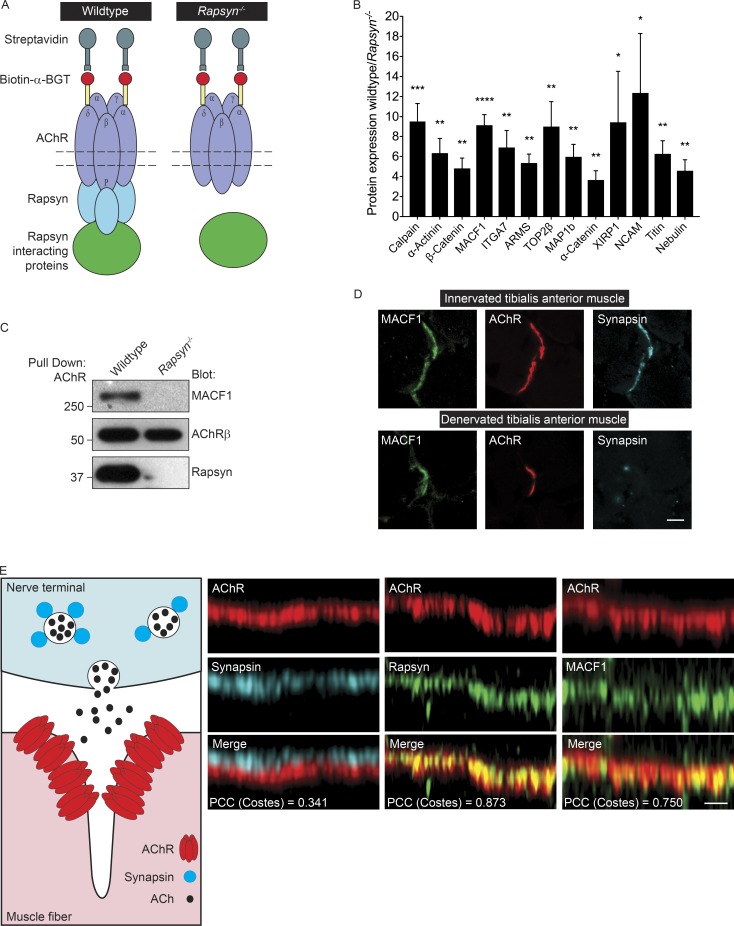
Figure 1.
MACF1 coisolates with AChRs in a Rapsyn-dependent manner. (A) The cartoon illustrates the procedure for isolating proteins that depend on Rapsyn for their coisolation with AChRs. (B) The proteins that associated with AChRs in a Rapsyn-dependent manner were 3- to 12-fold more abundant in AChR complexes isolated from WT than Rapsyn mutant muscle cells. The mean ± SEM values from six independent experiments are shown (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.005; ***, P < 0.0005; ****, P < 0.00005). (C) MACF1 coisolates with AChRs in a Rapsyn-dependent manner. (D) MACF1 (green) colocalizes with AChRs (red) and Synapsin (cyan) in cross-sections of innervated adult tibialis anterior muscle. MACF1 staining persists at denervated synaptic sites. Bar, 5 µm. (E) The cartoon illustrates that presynaptic Synapsin is separated by postsynaptic AChRs by >50 nm. As such, the positions of AChRs (red) and Synapsin (cyan) can be resolved in optical sections of the neuromuscular synapse. MACF1 (green) is present at the AChR-rich postsynaptic membrane (red) and not in nerve terminals. Bar, 2 µm. Colocalization of AChRs with Rapsyn (0.873 ± SEM 0.004), MACF1 (PCC = 0.750 ± SEM 0.021), and Synapsin (PCC = 0.341 ± SEM 0.021) were determined using PCC.