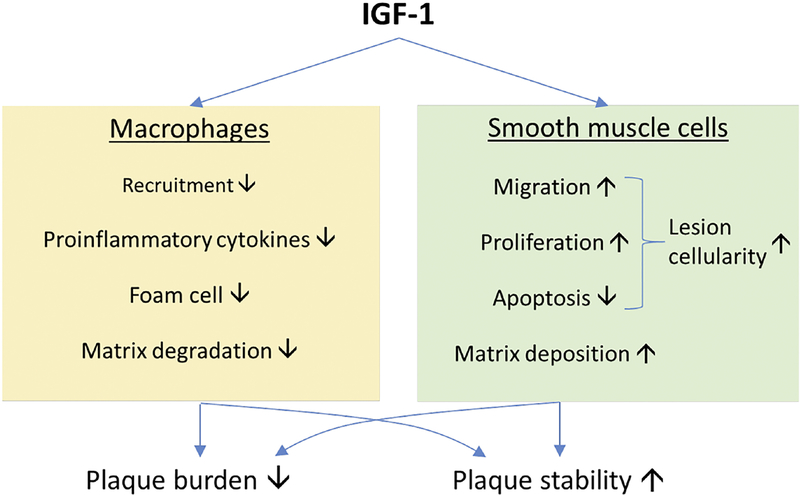
Figure. Cell-specific mechanisms underlying atheroprotective effect of IGF-1.
Cumulative reports of in vitro and in vivo investigations suggest that IGF-1 is suppressive to the recruitment of monocytes/macrophages to atherosclerotic plaques, production of proinflammatory cytokines, conversion of macrophages into lipid-laden foam cells, and extracellular matrix degradation. On the other hand, IGF-1 promotes smooth muscle cell (SMC) migration, proliferation and SMC-dependent matrix deposition. These cell-specific mechanisms may contribute to IGF-1-induced reduction in plaque burden and increase in plaque stability.