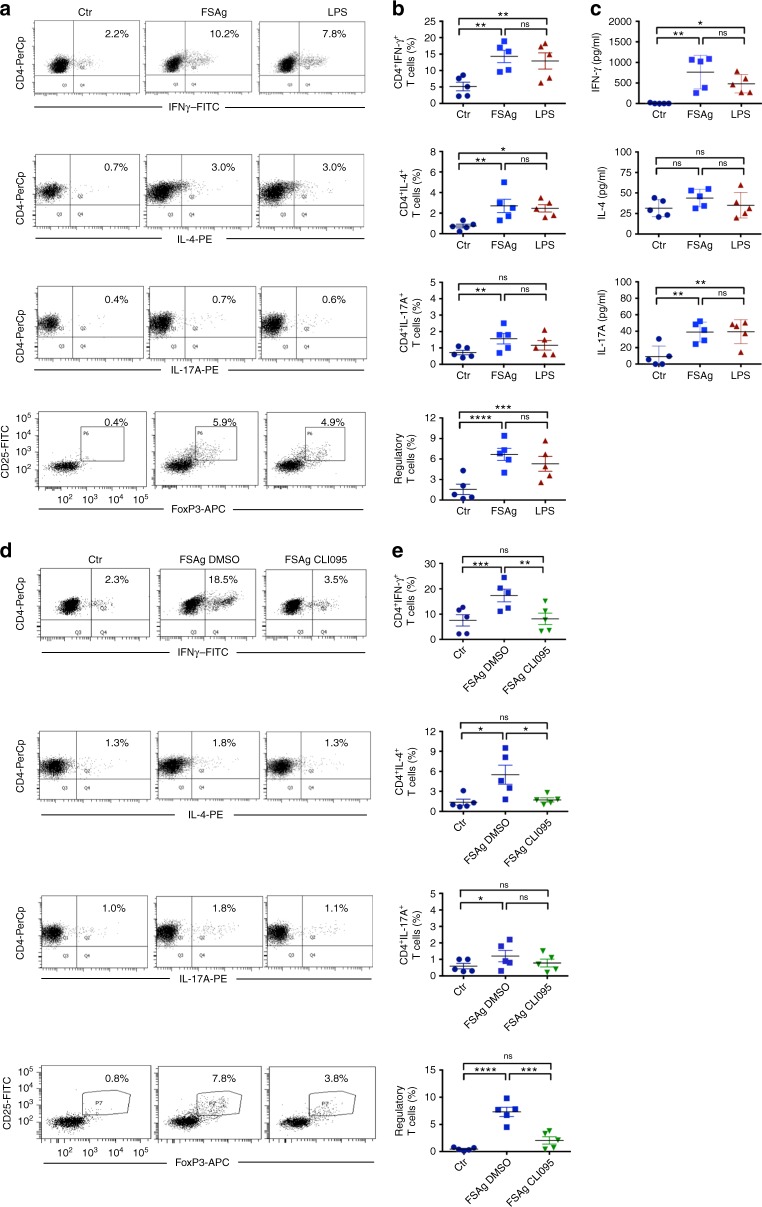
Fig. 6.
W. bancrofti sheath antigen-stimulated dendritic cells induce predominantly Th1 and regulatory T cell responses by TLR4-dependent mechanism. a–b W. bancrofti sheath antigen (FSAg)-activated dendritic cells were co-cultured with autologous CD4+ T cells for five days. Polarization of Th1, Th2, Th17, and regulatory T cell responses was analyzed by intracellular staining for IFN-γ, IL-4, IL-17A, and FoxP3, respectively. Representative dot-plots and mean ± SEM (n = 5 donors) values are presented. c Amount (pg/ml) of secretion of CD4+ T-cell cytokines IFN-γ, IL-4, and IL-17A in the dendritic cell–T cell co-cultures (mean ± SEM, n = 5 donors). d–e Inhibition of TLR4-signaling in dendritic cells abrogates T cell polarizing capacity of FSAg. Representative dot-plots for various CD4+ T cell subsets by intracellular staining for IFN-γ, IL-4, IL-17A, and FoxP3, and mean ± SEM (n = 5 donors) values are presented. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001; ns, not significant as analyzed by one-way ANOVA test. Abbreviation: Ctr, control