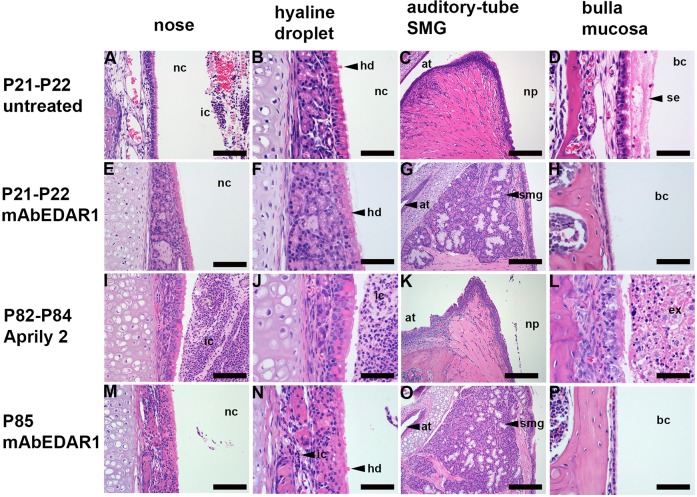
Fig. 1.
Prenatal treatment with agonist anti-EDAR antibody rescues auditory-tube submucosal glands (SMGs) and otitis media in EdaTa mice. (A-D) Untreated P21 EdaTa mice. (E-H) P21-P22 EdaTa mice treated with agonist anti-EDAR antibody (mAbEDAR1). (I-L) P82-P84 EdaTa mice treated with isotype control Aprily-2 (mouse IgG1 anti-hAPRIL). (M-P) P85 EdaTa treated with mAbEDAR1. Rhinitis (A,I,J) is characterised by heavy inflammatory cell exudation into the nasal cavity and is prevented (E,F) by mAbEDAR1 treatment except in a single P85-treated mouse shown (M,N), in which there is light infiltration of mucosa with inflammatory cells (shown in N). (B,F,J,N) Hyaline droplet change in nasal respiratory epithelium occurs in untreated, mAbEDAR1 and Aprily-2-treated mice. mAbEDAR1 rescues auditory-tube SMGs (G,O) and prevents otitis media (H,P). Otitis media is characterised by serous effusion in untreated P21 EdaTa mice (D) and suppurative exudation in Aprily-2-treated P85 EdaTa mice (L), whereas (H,P) P21 and P85 EdaTa mAbEDAR1-treated mice have healthy air-filled bulla cavity lined by slender mucosa. Panels E and F, I and J, K and L, and M and N are low- and high-magnification image pairs. at, auditory tube; bc, bulla cavity; ex, exudate; hd, hyaline droplets; ic, inflammatory cells; nc, nasal cavity; np, nasopharynx; se, serous effusion; smg, submucosal gland. Scale bars: (C,G,K,O) 200 µm; (A,E,I,M) 100 µm; (B,D,F,H,J,L,N,P) 50 µm.