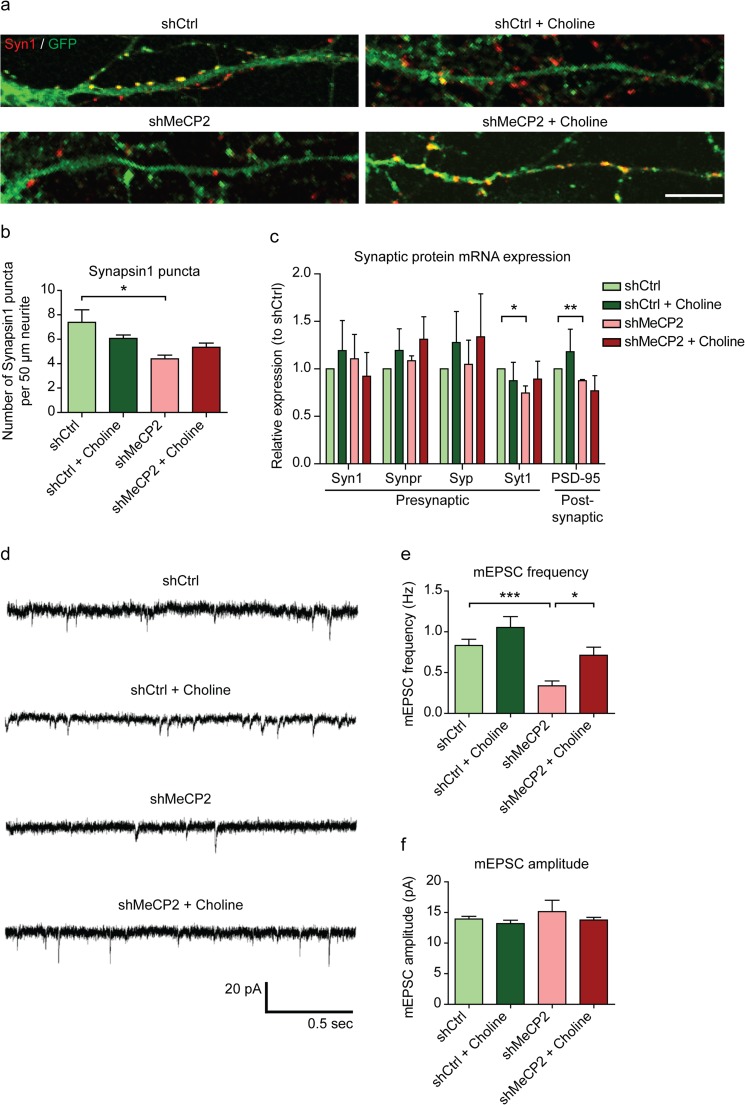
Fig. 4.
Choline supplementation restores synaptic defects in shMeCP2 neurons a Representative images of Synapsin1+ puncta (red) on GFP+ neurites (green) of DIV 14 cortical neurons. Co-localized puncta (yellow) were quantified. Scale bar represents 10 μm. b Quantification of Synapsin1+ puncta per 50 μm of neurite length. n = 3 cultures. c mRNA expression of selected presynaptic and postsynaptic proteins in shCtrl and shMeCP2 neuronal cultures with or without choline supplementation. Expression levels were normalized to the housekeeping gene Gapdh, and expressed relative to shCtrl levels. n = 5 cultures. Syn1, Synapsin1; Synpr, Synaptoporin; Syp, Synaptophysin; Syt1, Synaptotagmin1; PSD-95, Postsynaptic density 95. d Representative miniature excitatory postsynaptic current (mEPSC) recordings from shCtrl and shMeCP2 DIV 14 hippocampal neurons with or without choline supplementation. e and f Graphs show mean mEPSC frequency e and amplitude f of shCtrl and shMeCP2 neurons with or without choline supplementation. n = 19–35 neurons from six cultures. All values are presented as mean ± s.e.m. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 and *** p < 0.001. One-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-hoc