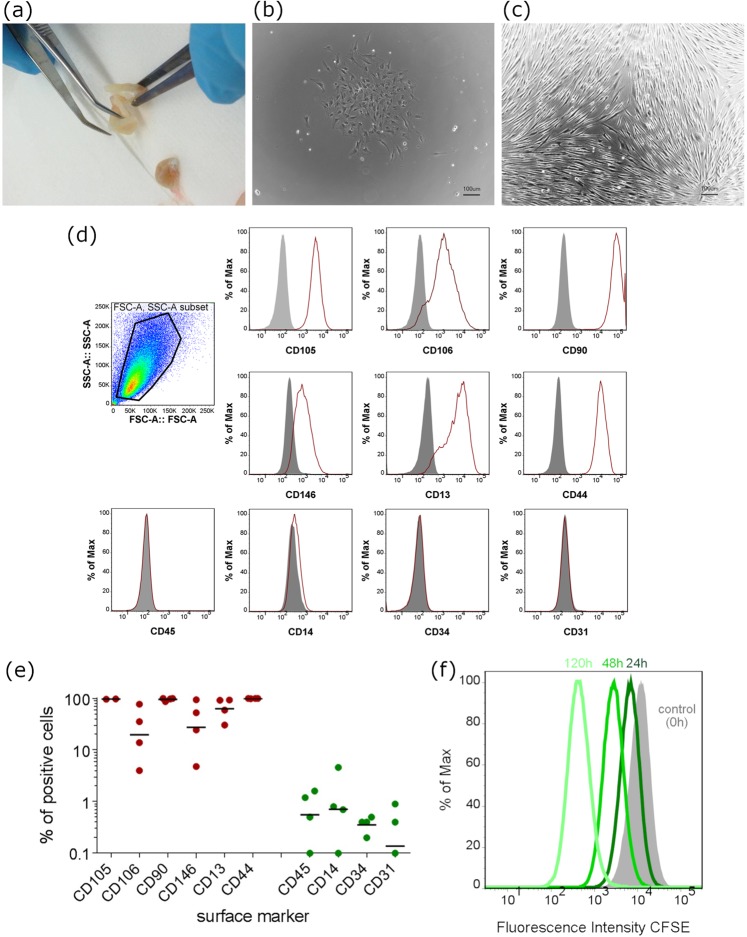
Figure 1.
Isolation and characterization of dental pulp cells. (a) Isolation of dental pulp from tooth specimen, (b) colony formation of in vitro cultivated DPCs 72 hours after isolation, (c) confluent layer of DPCs in standard cell culture condition and clearly visible fibroblastic morphology of expanded cells. (d) Surface marker expression of expanded DPCs in vitro (N = 4). The histograms represent individual experiments where surface marker expression of individual donors was quantified by flow cytometry for the positive and negative mesenchymal stromal markers. Cells (P1) were positive for CD105, CD106, CD90, CD146, CD13 and CD44, but negative for CD45, CD14, CD34 and CD31. (e) The percentage of positive cells for the respective surface markers is depicted. The middle left graph shows the gating strategy for alive DPCs. (N = 4 biological replicates). (f) Population doubling was assessed by CFSE assay with measured time points of 0 hours, 24 hours 72 hours and 120 hours. CFSE intensity was lowered due to cell division and thereby a doubling time of 24.99 hours was calculated.