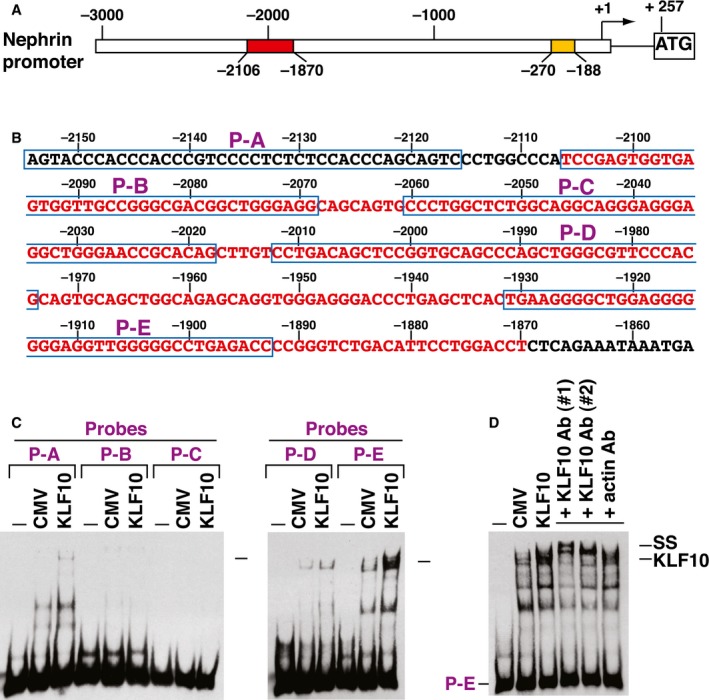
Figure EV2. EMSA analysis of KLF10 binding to the nephrin promoter region.
-
ASchematic diagram of mouse nephrin gene promoter. The transcriptional start site of mouse nephrin gene promoter (GenBank: AF190638.1) is located 257‐bp upstream of the ATG codon. Two evolutionarily conserved promoter regions essential for podocyte‐specific expression are indicated by yellow (from −188 to −270; 83‐bp region) and red (from −1,870 to −2,106; 237‐bp region) boxes, respectively. The 83‐bp nephrin promoter element contains a WT‐1 binding site, whereas the 237‐bp promoter element contains multiple potential Sp1 binding sites.
-
BDNA sequence of the promoter region encompassing the 237‐bp promoter region (from −1,870 to −2,106; red color) and the localization of five non‐overlapping probes (P‐A, P‐B, P‐C, P‐D, and P‐E) used in EMSAs.
-
CEMSAs of KLF10 binding to nephrin promoter elements. EMSA experiments were performed by using nephrin promoter elements (including P‐A, P‐B, P‐C, P‐D, and P‐E) and protein lysates of 293T cells that were transfected with an empty vector or KLF10‐expressing plasmid. Arrows indicated the potential KLF10/DNA complexes in EMSA experiments.
-
DSupershift analysis of the KLF10/DNA complex in EMSA. Different antibodies against KLF10 were used to supershift the formed complex in EMSA experiments using the P‐E element as a probe. Anti‐KLF10 antibody #1 was a kind gift from Dr. Vincent H.S. Chang, whereas anti‐KLF10 antibody #2 (ab73537; Abcam) was obtained commercially.
