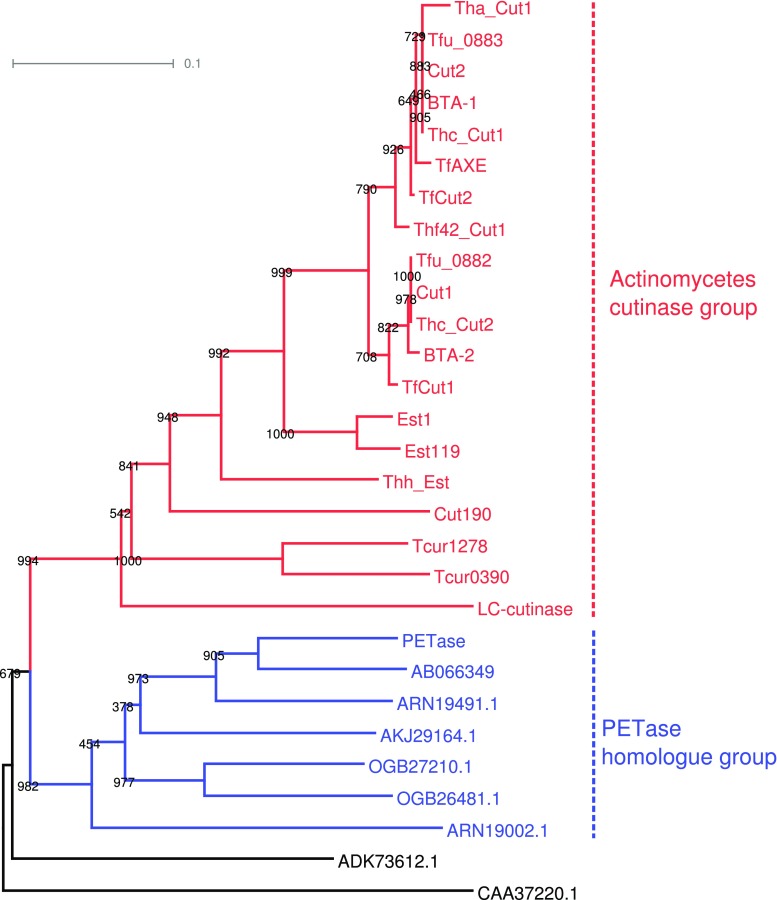
Fig. 2.
Phylogenetic tree for amino acid sequences of the reported PET hydrolases and their homologs. A multiple alignment and a tree were constructed using the program ClustalW2 (Larkin et al. 2007). The tree was generated by the neighbor-joining algorithm using sites without any gaps and was displayed as a midpoint-rooted tree using the program Dendroscape 3 (Huson and Scornavacca 2012). Numbers on the ancestor nodes are bootstrap values calculated by 1000 bootstrap samples. Actinomycete cutinases are represented using the enzyme names shown in Table 1. Six additional homologs for PETase were taken from the UniProt/TrEMBL database. GenBank accession AB066349 is poly(tetramethylene succinate) depolymerase from Acidovorax delafieldii (Uchida et al. 2002). The other five accession IDs are uncharacterized proteins found in bacteria as follows: ARN19491.1 and ARN19002.1 are from Rhizobacter gummiphilus, OGB27210.1 and OGB26481.1 are from Burkholderiales bacterium, and AKJ29164.1 is from Polyangium brachysporum. Two remote bacterial homologs (ADK73612.1 and CAA37220.1) were included to determine the root. ADK73612.1 is cutinase A from Pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes, and CAA37220.1 is lipase 1 from Moraxella sp. (strain TA144)