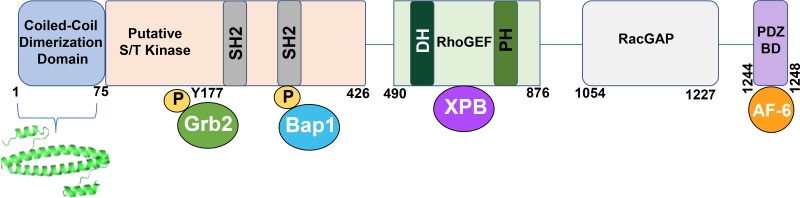
Figure 3. A schematic representation of the BCR protein.
BCR consists of an anti-parallel coiled-coil dimerization domain, within amino acids 1–75. Directly below is the crystal structure for this domain, depicted as a dimer (PDB 1K1F). The putative serine/ threonine kinase domain is portrayed through residue 426. This domain contains two SH2 binding sites, which interact with ABL SH2 domains. The adapter protein Grb2 binds to phosphorylated Y177 on BCR, and Bap1 also interacts with BCR via phosphorylated serine residues present in the second SH2 binding site. The RhoGEF domain is shown, containing Dbl Homology (DH) and Pleckstrin Homology (PH) domains, typical of a GEF. XPB associates with the GEF domain. The RacGAP domain encompasses amino acids 1054–1227, while the PDZ binding domain binds to AF-6 through the S-T-E-V motif found in the C-terminus of BCR. PDZ domains are named for three proteins that share the domain; Post synaptic density protein (PSD95), Drosophila Disc large tumor suppressor (Dlg1), and Zonula occludens-1 protein (zo-1). The associated proteins shown are: Grb2, Growth factor receptor-bound protein 2; Bap1, BRCA1 associated protein-1 (ubiquitin carboxy-terminal hydrolase); XPB, Xeroderma Pigmentosum type B (an ATP-dependent DNA helicase).