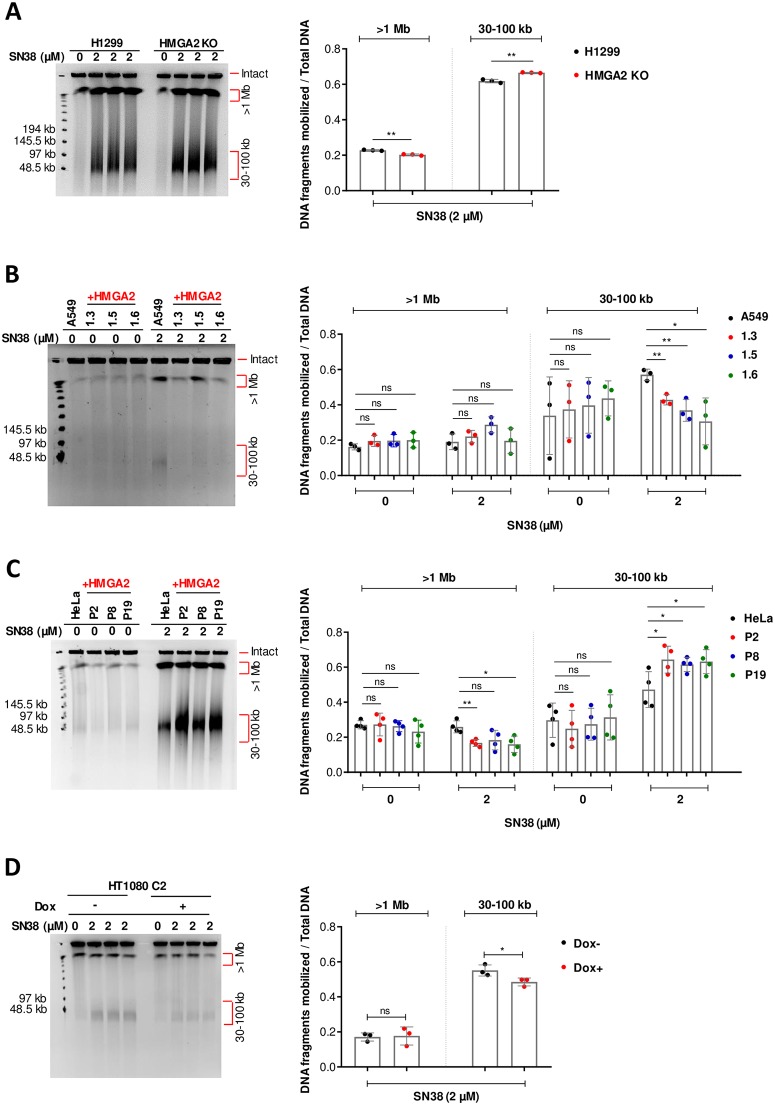
Fig 2. HMGA2 expression controls sensitivity to TOP1 poison SN38.
(A) PFGE analysis of DSB formation in H1299 cells (parental and HMGA2 KO) in response to 48 h incubation with SN38 (left panel). Quantification of SN38-induced DNA fragments (>1 Mb and 30–100 kb fractions) was done by ImageJ software (right panel) with each fragment fraction normalized to total DNA loaded (n = 3 independent experiments). Error bars show SD. Unpaired two-tailed t-tests. ** p < 0.01. (B) Representative PFGE analysis of DSB formation in A549 cells (parental and three recombinant human HMGA2-expressing cell lines) in response to 48 h incubation with SN38 (left panel). Quantification of SN38-induced DNA fragments (>1 Mb and 30–100 kb fractions) (right panel) was done by ImageJ software with each fragment fraction normalized to total DNA loaded (n = 3 independent experiments). Error bars show SD. Unpaired two-tailed t-tests. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01. (C) Representative PFGE analysis of DSB formation in HeLa cells (parental and three recombinant human HMGA2-expressing cell lines) in response to 48 h incubation with SN38 (left panel). Quantification of SN38-induced DNA fragments (>1 Mb and 30–100 kb fractions) (right panel) was done by ImageJ software with each fragment fraction normalized to total DNA loaded (n = 4 independent experiments). Error bars show SD. Unpaired two-tailed t-tests. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01. (D) Representative PFGE analysis of DSB formation in HT1080 C2 cell line in response to 48 h incubation with SN38 (left panel). HMGA2 expression was down-regulated by doxycycline (Dox)-induced shRNA for 96 h in conjunction with SN38 treatment for the last 48 h. Quantification of SN38-induced DNA fragments (>1 Mb and 30–100 kb fractions) was done by ImageJ software (right panel) with each fragment fraction normalized to total DNA loaded (n = 3 independent experiments). Error bars show SD. Unpaired two-tailed t-tests. * p < 0.05.