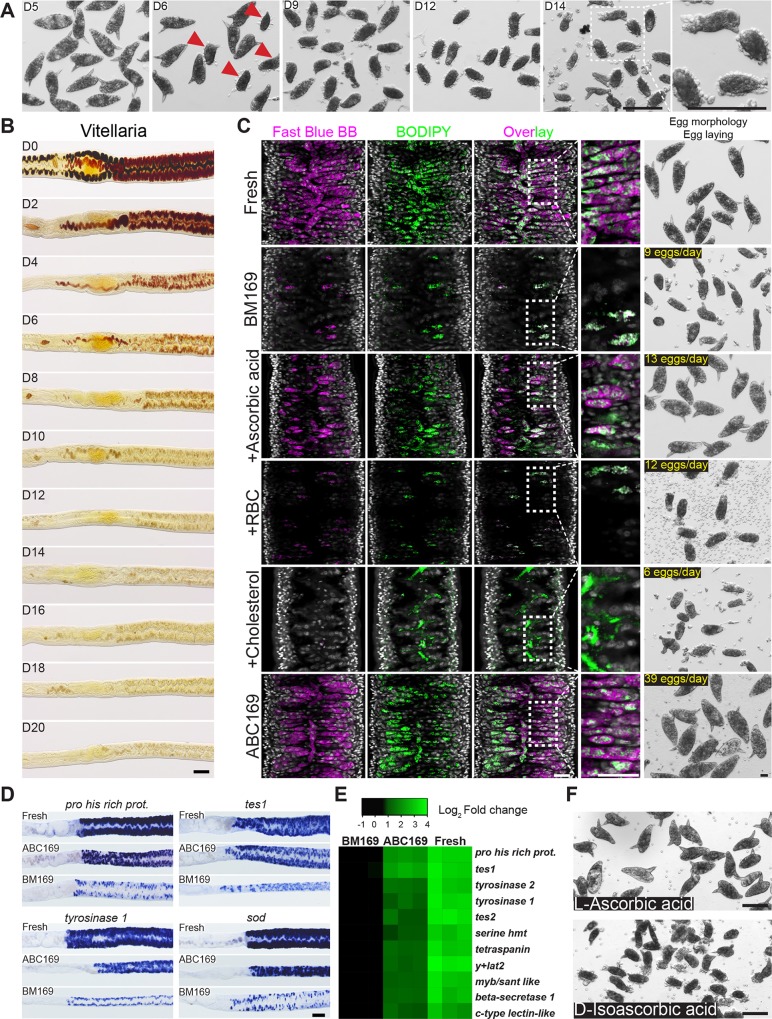
Fig 1. ABC169 supports the maintenance of schistosome vitellaria.
(A) Morphological changes of eggs laid by worm pairs maintained in BM169. After D6, parasites began laying abnormally formed eggs (arrow). These eggs were small, usually did not contain a lateral spine, and did not possess a smooth surface. (B) Fast Blue BB staining (brownish-red labeling) showing loss of mature vitellocytes during culture in BM169. Representative images from 3 experiments with n > 10 parasites. (C) Confocal slice showing Fast Blue BB and BODIPY labeling of vitelline and lipid droplets in the vitellaria, respectively. Shown are freshly recovered parasites (“Fresh”) and schistosomes at D20 of cultivation in BM169 supplemented with RBCs, LDL supplement (Cholesterol), or ascorbic acid. ABC169 represents the combination of RBCs, LDL supplement, and ascorbic acid. Representative images from 3 experiments with n > 10 parasites. (D) Whole-mount in situ hybridization showing expression of vitellaria-enriched genes in freshly perfused female worms and parasites cultured in ABC169 or BM169 for 20 days. Representative images from 3 experiments with n ≥ 9 parasites. (E) Heatmap showing relative expression of vitellaria-enriched transcripts in freshly perfused female worms (“Fresh”) and parasites cultured in ABC169 or BM169 for 20 days. Each column represents an independent biological replicate; samples are normalized to the expression of an arbitrarily chosen biological replicate from the BM169 group. Changes in expression between each of the 11 genes in BM169 and ABC169 were statistically significant (p < 0.05, t test). Underlying primary data can be found in S1 Data. (F) Morphology of eggs laid by paired adult females in ABC169 supplemented with L-ascorbic acid or D-isoascorbic acid on D20. Representative of 3 experiments. Scale bars: A, B, D, F, 100 μm; C, 25 μm. ABC169, Ascorbic Acid, Blood Cells, Cholesterol, and BM169; BM169, Basch’s medium 169; BODIPY, boron dipyrromethene; D, day; LDL, low-density lipoprotein; myb/sant like, Myb/SANT-like DNA-binding domain-containing protein; RBC, red blood cell; sod, extracellular superoxide dismutase [Cu-Zn]; tes, trematode eggshell synthesis protein; y+lat2, Y+L amino acid transporter 2.