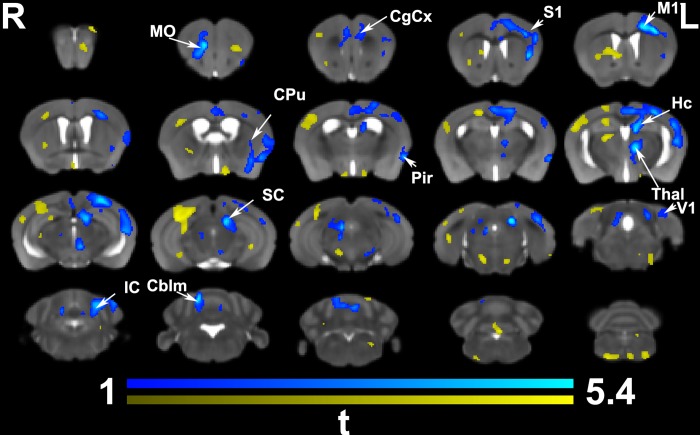
Fig 3. In vivo voxel based morphometry identified areas of significant enlargement in trained animals relative to the controls.
These areas were found in the bilateral medial orbital cortex (MO) and cingulate cortex (CgCx) (A32), as well is in the contralateral (left) cingulate cortex (A24, and 29), primary motor (M1), somatosensory (S1), caudate putamen (CPu), and hippocampus (Hc); and the visual (V1) cortex. In addition, clusters of hypertrophy covered areas of the thalamus (Thal; e.g. the parafascicular and mediodorsal nuclei), the superior (SC) and inferior colliculi (IC), and cerebellum (Cblm). The ipsilateral piriform cortex (Pir) was enlarged. Results are presented as tmaps, FDR cluster-corrected for multiple comparisons using an initial cluster forming threshold of 0.05 significance and the whole brain as a mask (blue color). Uncorrected statistical maps (shown in yellow) suggested involvement of the ipsilateral hemisphere as well.