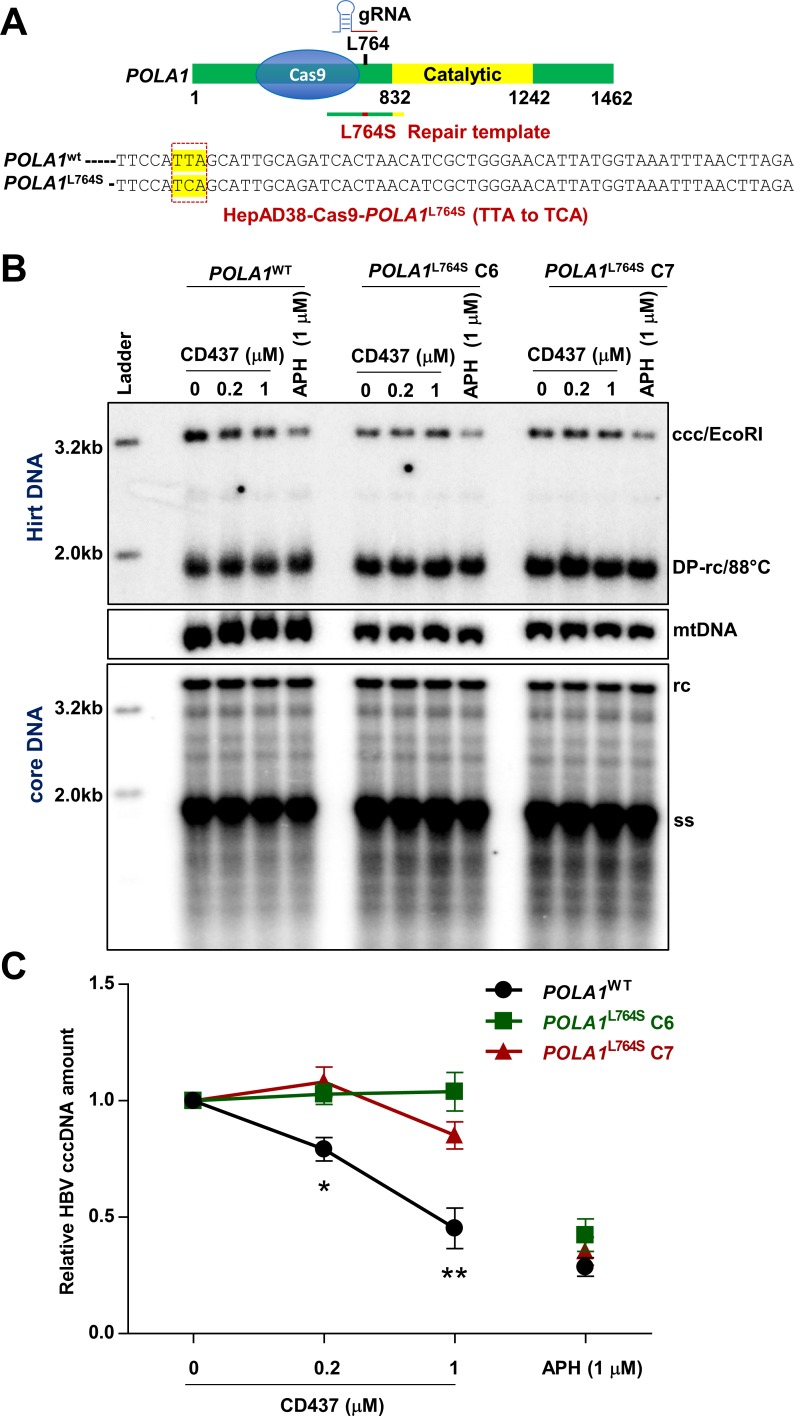
Fig 4. Single amino acid substitution of Pol α abolishes CD437 inhibition of cccDNA synthesis.
(A) Schematic representation of CRISPR Knock-in strategy to generate HepAD38-Cas9-POLΑ1L764S cells. The DNA sequencing results are highlighted to indicate the successful editing of TTA to TCA which results in L764S mutation. (B) HepAD38-Cas9-POLΑ1WT and two independent clones of HepAD38-POLΑ1L764S C6 and C7 were cultured in the presence of 2 mM PFA from day 2 to day 6 after tet removal. On day 6, cccDNA synthesis was resumed by removing PFA and the cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of CD437 or APH started at the removal of PFA for 24 h. Cytoplasmic HBV core DNA and Hirt DNA were extracted and detected by Southern blot assays, with mtDNA as a loading control of Hirt DNA. (C) The intensity of HBV cccDNA band was quantified by ImageJ and presented as relative amount in comparison with that in mock-treated correspondent cell. Data represent 4 independent experiments (mean ± SEM). Data were analyzed by two-tailed Student’s t-test (unpaired), *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.