Figure 1.
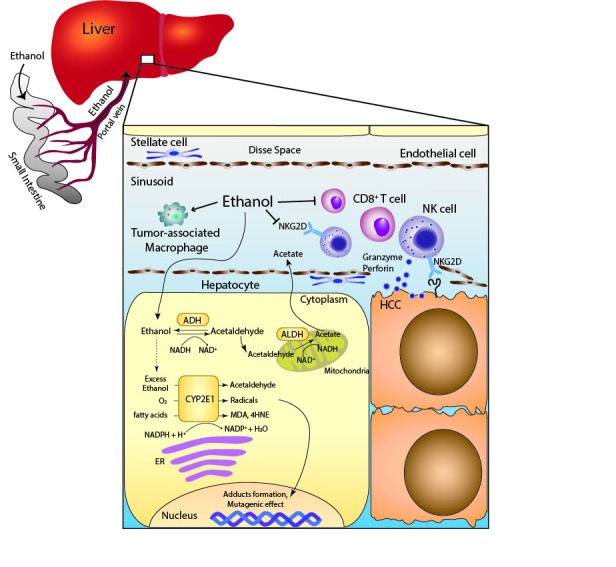
Scheme of the immune system in HCC surveillance and the metabolic effects of alcohol exposure on hepatocyte. The metabolism of ethanol through the CYP2E1-dependent pathway produces acetaldehyde, radicals and lipid peroxidation products, such as MDA and 4HNE. Alcohol consumption reduces the number of CD8+ T cells and NK cells, and reduces the NKG2D expression on NK cells. 4HNE, 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal; ADH, alcohol dehydrogenase; ALDH, aldehyde dehydrogenase; CYP2E1, cytochrome P450 2E1; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; MDA, malondialdehyde; NK, natural killer; NKG2D, NK group 2D.
