Figure 2.
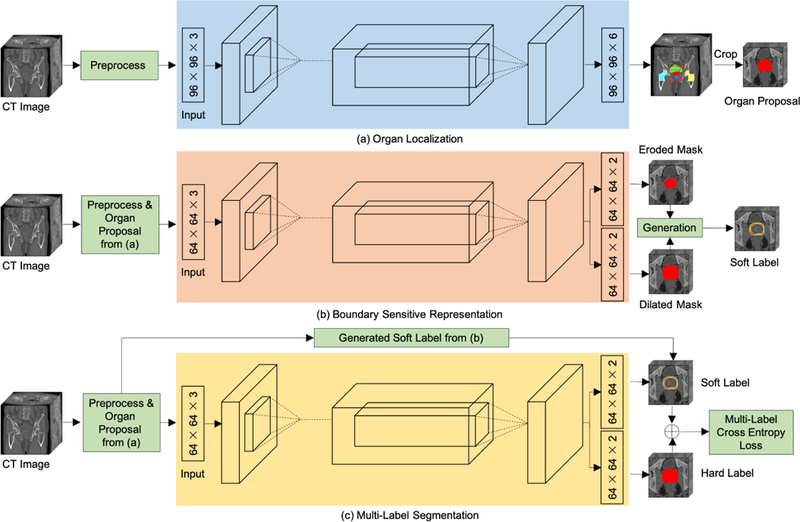
An illustration of the proposed framework for prostate, bladder, and rectum segmentations in CT images (with the prostate segmentation as an example). (a) Organ proposals of raw CT images are first generated by an organ localization network to focus on the candidate regions. (b) Then, a boundary sensitive representation network with multi-task learning is trained to generate soft boundary labels of the corresponding organ proposals. (c) Finally, a multi-task network that uses soft labels and hard labels as supervision is learned to perform voxel-wise segmentation in organ proposals.
