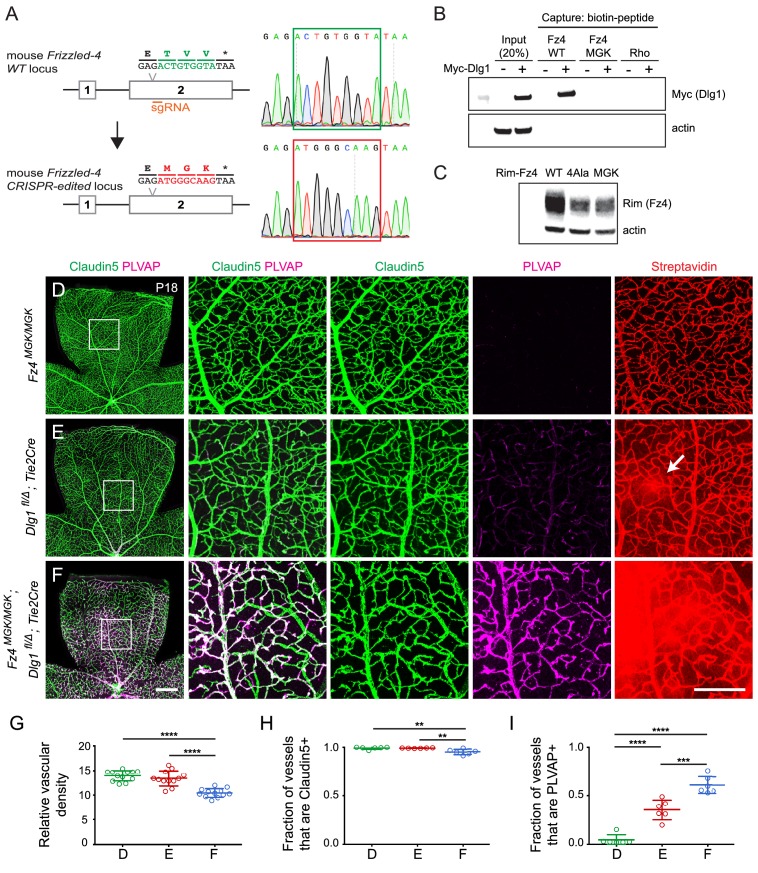
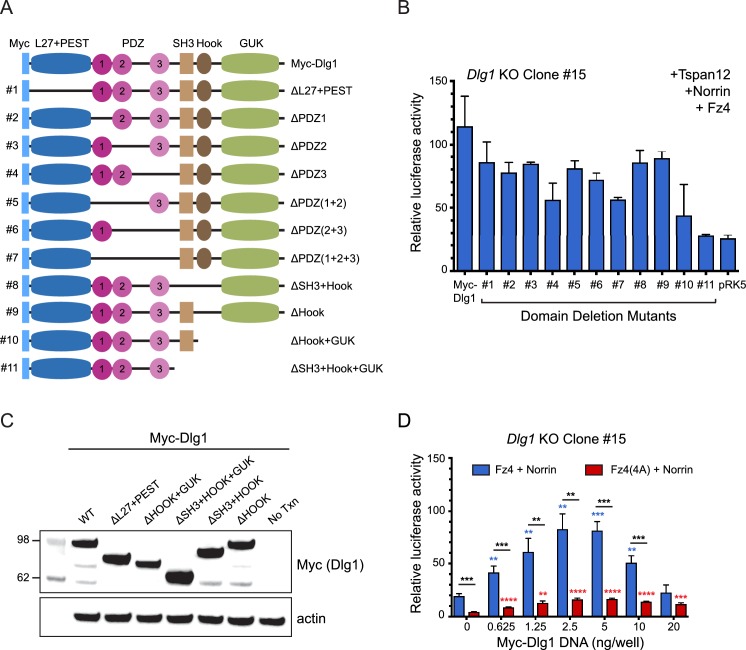
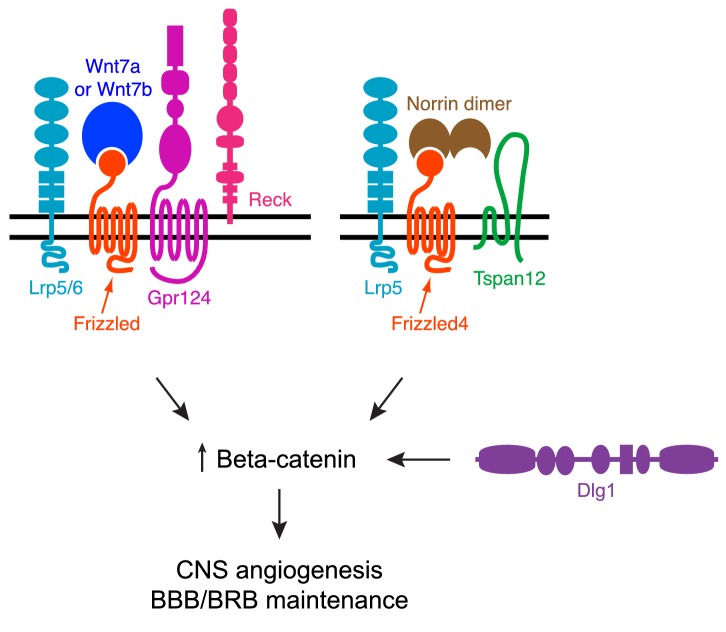
Figure 8. Mutation of the Fz4 C-terminal PDZ-binding domain enhances the severity of retinal vascular defects in a Dlg1 mutant background.
(A) Diagram of the Fz4 allele produced by CRISPR/Cas9 editing (Fz4MGK). Numbers indicate exons. TVV, the C-terminal three amino acids, were substituted with MGK. Right, sequencing chromatograms from mouse tail PCR products. Boxes encompass the three altered codons. Top, WT allele. Bottom, Fz4MGK allele. (B) Protein extracts from HEK/293T cells transfected with WT Myc-Dlg1 (+) or an empty expression vector (–) were subjected to affinity capture using a biotin-Fz4 WT C-terminal peptide, a biotin-Fz4 peptide with the C-terminal three amino acids substituted by MGK, or a biotin-rhodopsin C-terminal peptide. Myc-Dlg1 binds only to the Fz4 WT C-terminal peptide. (C) Immunoblot of protein extracts from HEK/293T cells transfected with Rim-Fz4 WT, Rim-Fz4(4A) or Rim-Fz4(MGK), i.e., Fz4 with the C-terminal three amino acids changed to MGK. (D–F) Maximum projection of the superficial, intermediate, and deep vascular plexuses of P18 retinas from the indicated genotypes (column 1) with boxed regions enlarged in columns 2–5. Mice were injected IP with 2–3 mg of sulfo-NHS-biotin 1–2 hr before sacrifice. Arrow in (E) indicates biotin leakage. Scale bar for column 1, 400 μm. Scale bar for columns 2–5, 200 μm. (G–I) Quantification of summed vascular density (G), the fraction of vessels that immunostain for Claudin5 (H), and the fraction of vessels that immunostain for PLVAP (I), for the genotypes shown in (D–F).