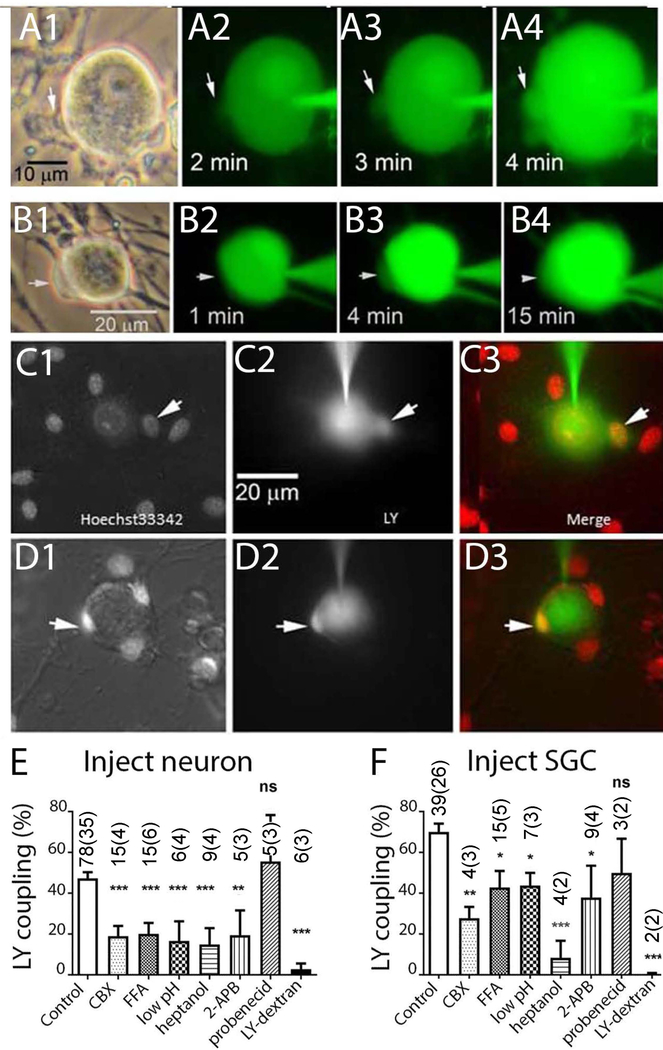
Figure 5. Lucifer Yellow (LY) injections performed in dissociated cultures of trigeminal ganglion demonstrate gap junction mediated coupling between neurons and SGCs.
A1–4 and B1–4 illustrate time course of dye spread into SGCs (arrows) during LY injection into neurons. C1–D3 illustrate two experiments in which LY was injected into neurons in cultures which were acutely treated with the nuclear indicator Hoechst 33342. Overlays in C3, D3 demonstrate LY presence in small SGCs that are closely apposed to the neuron surface. E, F. Summary of experiments in which incidence of LY dye coupling was quantified after injection into neurons (E) or SGC (F). Drugs applied were 200 μM CBX, 100 μM flufenamic acid (FFA), 2 mM heptanol, 100 μM 2-APB, 1 mM probenecid. Intracellular acidification (low pH) was obtained through application of solution bubbled with 100% CO2, LY Dextran (MW 10 Da), a large fluorescent gap junction impermeant molecule, was completely retained in the injected cell. * indicates p<0.05, ** p< 0.01 and *** p< 0.005 (Fisher’s exact test). The numbers in the bars indicate the number of cells injected. In the case of both SGC and neuron injections, most recipients of the dye injections were SGCs.