Fig. 3. Loss of Setdb1 disrupts telomeric binding of methylated lysine readers, histone chaperones, and recombination factors.
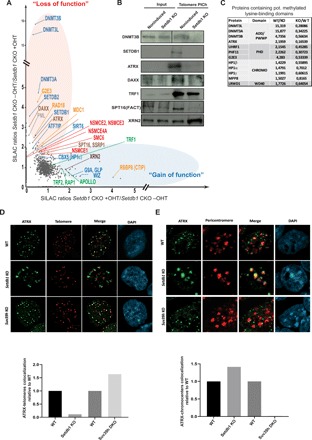
(A) qPICh plots showing changes in protein composition at telomeres upon SEDTB1 removal in mESCs. Major protein losses (in the red oval) and gains (in the blue oval) are highlighted. (B) Immunoblots using the indicated antibodies of purified telomeric extracts by PICh from noninduced wild-type cells or Setdb1 KO induced after 4 days of treatment with tamoxifen. An anti-SPT16 antibody was used to analyze FACT recruitment to telomeres. (C) qPICh SILAC in cell culture ratio values of proteins lost that contain putative methylated lysine-binding domains in Setdb1 KO mESC. (D) Top: ATRX (green) immunostaining combined with telomere fluorescence in situ hybridization staining (red) in wild-type or Setdb1- and Suv39h-negative mESCs. Bottom: Quantification of the loss or the gain of colocalization of ATRX-telomere signals relative to wild-type colocalization values. (E) Top: ATRX (green) immunostaining combined with pericentromere fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) (red). Bottom: Quantification of the loss or the gain of colocalization of ATRX-pericentromere signal relative to the wild-type colocalization values.
