Fig. 4. Telomeric H3K9me3 levels correlate with telomere transcription.
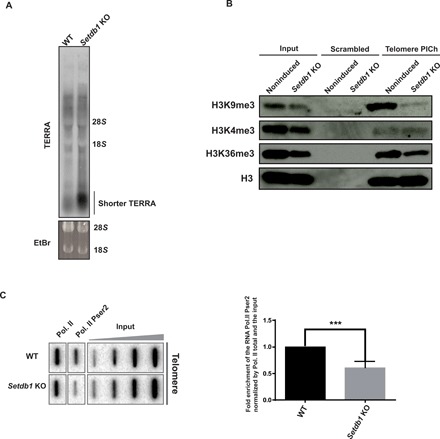
(A) TERRA Northern blot of wild-type or Setdb1-knockout cells. TERRAs were detected with (CCCTAA)6-radiolabeled probes. Ethidium bromide (EtBr) signals were used as loading controls. Signal intensities for TERRA species below 1000 nucleotides in wild-type versus Setdb1 KO lanes were compared. (B) Immunoblots of scramble or telomere PICh for the analysis of the enrichment of several histone modifications H3K9me3, H3K4me3, and H3K36me3 at telomeres upon SETDB1 removal. (C) ChIP experiments using antibodies raised against total RNA polymerase II (Pol. II) and against its phosphorylated serine 2 (Pser2) of its C-terminal domain in noninduced wild-type and Setdb1 knockout mESCs. Twenty percent of the immunoprecipitated DNA was blotted and probed with a telomere-specific probe. Inputs of 0.01, 0.05, 0.25, and 1.25% were loaded. Bottom: Quantifications representing the fold enrichment of the CTD phosphorylation at serine 2 of the RNA polymerase II in Setdb1 knockout cells normalized by the total RNA polymerase II signals at telomeres and the input relative to the wild type. ***P = 0.005, Student’s t test.
