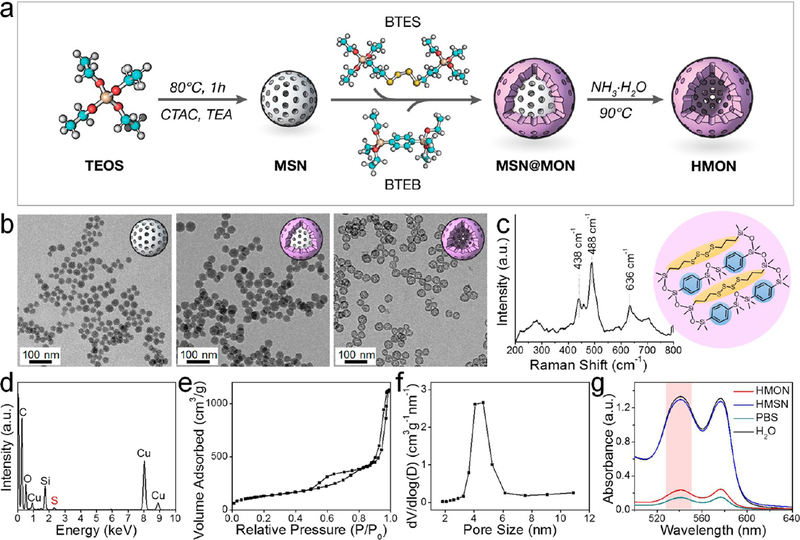
Figure 1.
Preparation and characterization of sub-50 nm thioether/phenylene dual-hybridized HMON. (a) Schematic synthesis route. MSN was first synthesized as a hard template. Through cohydrolysis of BTES and BTEB, core/shell structured MSN@MON was fabricated with thioether and phenylene moieties incorporated in the MON framework. The final HMON was fabricated via a special “ammonia-assisted hot water etching” strategy. (b) TEM images of MSN, MSN@MON, and HMON. Scale bar, 100 nm. (c) Raman spectrum. The shift at 438/488 and 636 cm−1 represented specific stretching vibrations of −S−S− bond and −S−C− bond, respectively. Insert: schematic illustration of the thioether/ phenylene dual-hybridized framework. (d) Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) spectrum. (e) N2 adsorption−desorption isotherm and (f) corresponding pore-size distribution, which showed a large surface area of 475.2 m2/g and an average pore size of around 4.3 nm, respectively. (g) UV−vis spectra of supernatant after centrifugation of HMON or HMSN treated RBCs. Ultrapure water and PBS were set as the positive and negative control, respectively. The dual-hybridized HMON featured with significantly lower hemolysis relative to HMSN.