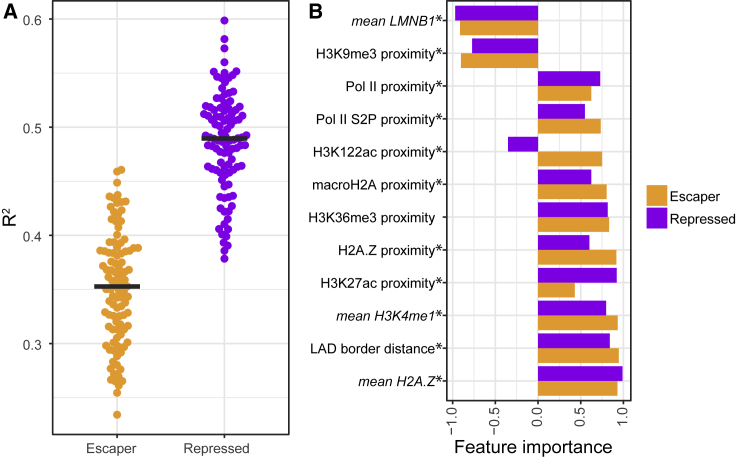
Figure 5.
Modeling TRIP Expression Levels as Function of LAD Chromatin Features
(A) R2 values of 100 lasso regression models of TRIP data for escaper and repressor promoters (see STAR Methods). Each dot represents a model. Black lines represent the median R2 values.
(B) Feature importance analysis of the most predictive chromatin features. Feature importance (x axis) represents the fraction of bootstrap-lasso models (out of 1,000), in which a feature contributed significantly to the model performance. Negative and positive values of feature importance reflect negative and positive coefficient values, respectively. Asterisks mark significant (p < 0.001) differences between repressed and escaper promoters. Mean signal intensities of chromatin features in a window around the integration site (5 kb for ChIP; 10 kb for DamID) as well as the proximity to the nearest peak of the same features were taken into account. The distributions of input values of all features that were tested are shown in Figure S4. Only data from integrations inside LADs of the three repressed and three escaper promoters were used.
See also Figures S3, S4, and S5, Data S2, and Table S2.