Figure 7.
IR and IGF-1R Inhibition Attenuates Entrainment of Circadian Rhythms to Feeding Time In Vivo
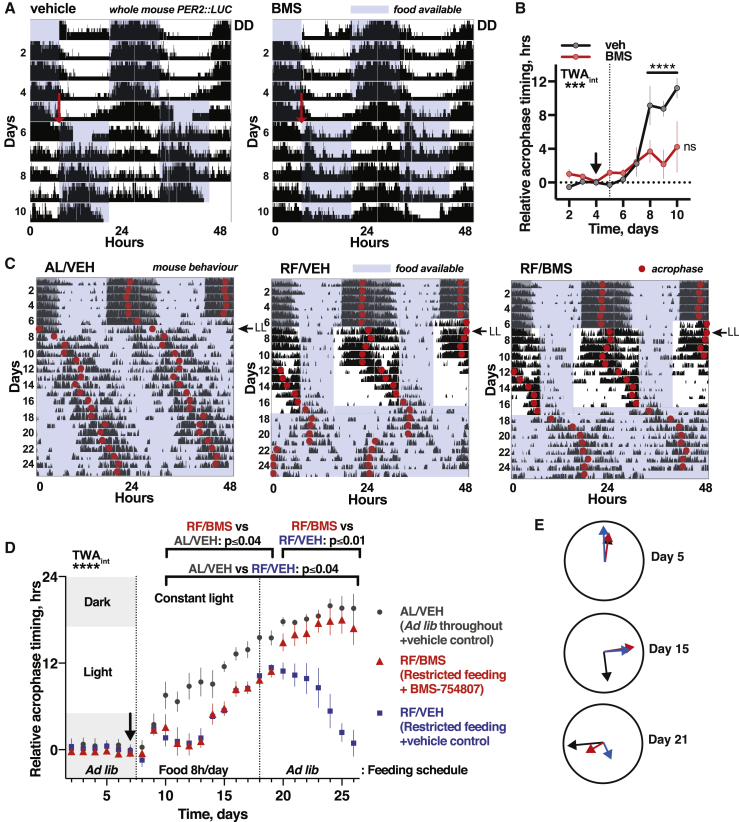
(A) Representative PER2::LUC bioluminescence for restricted fed (RF) mice, with 12 h delay in feeding time from day 5 (red arrow). BMS-754807 or vehicle provided in drinking water throughout.
(B) Shift in PER2::LUC acrophase following change in feeding schedule was significantly delayed for BMS-treated group, reported relative to acrophase on days 2–4 (n = 4, TWA, Tukey’s MCT).
(C) Mean wheel-running activity for mice entrained to 12 h:12 h LD cycles, then released to constant light (LL). Restricted feeding (RF) groups (n = 6) were fed 8 h/day for 9 days before return to ad lib feeding, with one RF group receiving BMS-754807 in drinking water from day 7. Control group freely fed throughout (left: n = 6).
(D) IR and IGF-1R inhibition attenuates temporal reorganization of daily rest-activity cycles after, not during, restricted feeding under LL (n = 6, TWA, Sidak MCT). Acrophase calculated relative to acrophase on final day of LD (black arrow).
(E) Mean acrophase before, during, and after RF (days 5, 15, and 21). Arrow lengths are inversely proportional to SEM.
See also Figure S7.