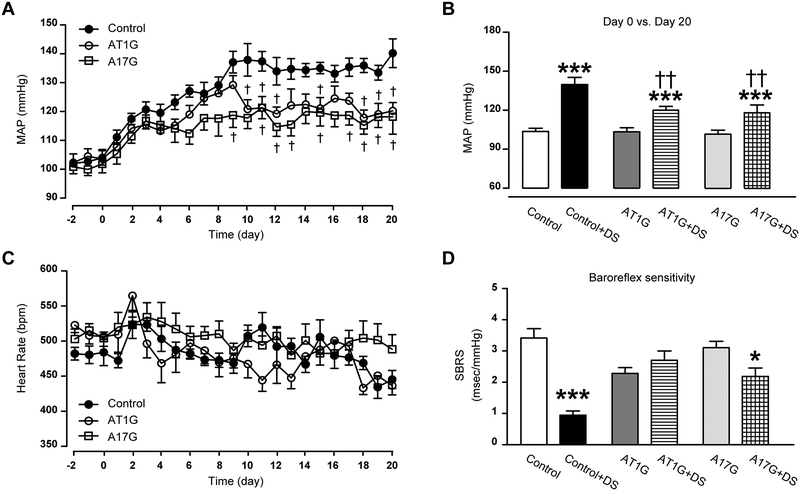
Figure 2. Knockdown of ADAM17 in glutamatergic neurons attenuates salt-sensitive hypertension.
(A) DOCA implanted subcutaneously (1 mg/g of body weight) and combined with 1% saline in the drinking water, induced a progressive increase in mean arterial pressure (MAP) in uninephrectomized control mice. This DOCA-salt-induced hypertension was blunted in both A17G and AT1G mice (n=10 mice/group). (B) Summary data for the MAP values, before and after 20 days of DOCA-salt treatment. (C) Changes in heart rate for control, AT1G and A17G mice over time. (D) Summary data for the spontaneous baroreceptor reflex sensitivity (SBRS), before and after 20 days of DOCA-salt treatment (n=10 mice/group). SBRS was calculated using the sequence method. Data are shown as mean ±SEM. Statistical significance: Two-way ANOVA, Bonferroni post hoc test: *P<0.05, ***P<0.001 vs. respective baselines; †P<0.05, ††P<0.01 vs. control+DS. DS: DOCA-salt.