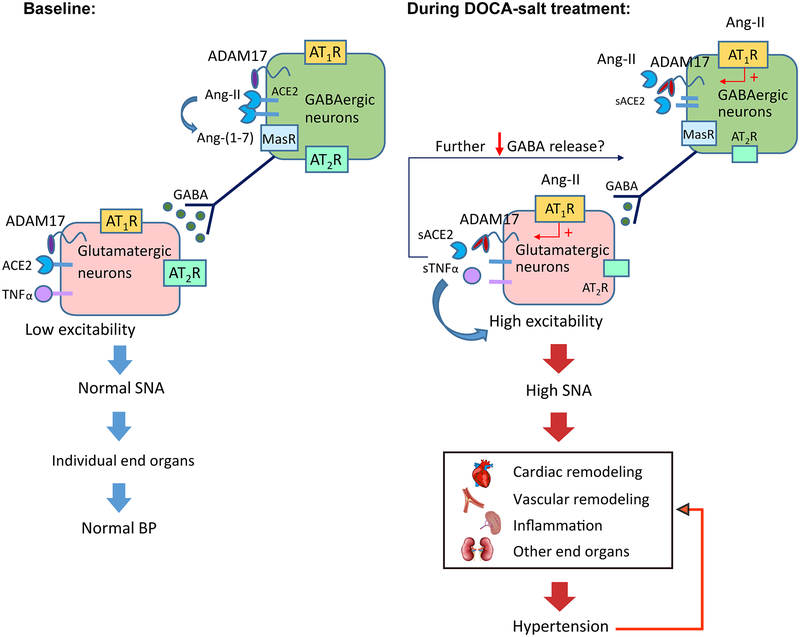
Figure 6. A working model explaining how neuronal ADAM17 support the development of salt-sensitive hypertension.
At baseline, sympathetic outflow and BP is controlled, due to the low excitability of pre-sympathetic glutamatergic neurons. Upon DOCA-salt treatment, up-regulated ADAM17 could increase the excitability of these neurons by releasing TNFα and compromising the compensatory activity of ACE2, therefore promoting sympatho-excitation. As result, cardiac output, vascular capacitance and resistance, and deployment of T cells from spleen are increased, inducing uncontrolled elevation of BP. With prolonged dysregulation of autonomic nervous system and BP, cardiovascular remodeling and peripheral inflammation are developed, further supporting the maintenance of hypertension.