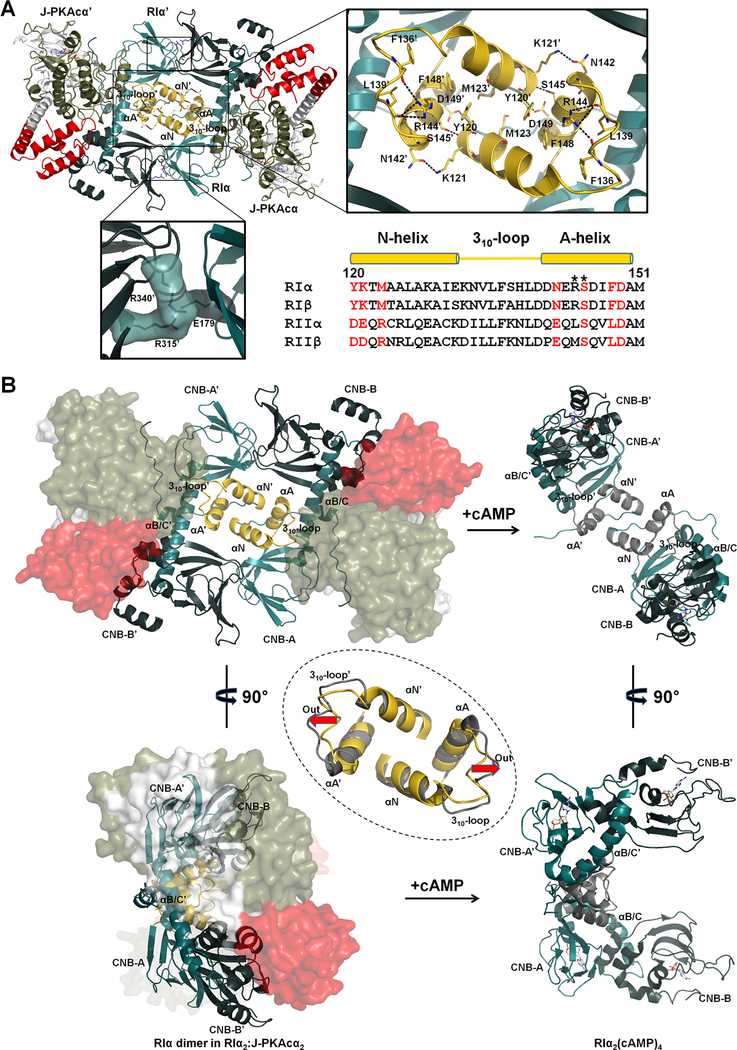
Figure 3. Interactions of the two RIα:J-PKAcα heterodimers in the chimeric holoenzyme.
(A) Overall interface of the two heterodimers consists of a large N3A-N3A’ interface and two identical small interfaces with salt bridges. Sequence alignment of the N3A motifs from different R isoforms is shown at the right bottom. Interface residues at the N3A motif are labeled in red. CNC mutations are marked with asterisks.
(B) The N3A-N3A’ four-helical bundle acts as a structural anchor during cAMP activation. The αB/C-helix and the CNB-B domain of RIα undergo dramatic conformational changes upon cAMP binding, while the N3A-N3A’ helical bundle is almost unaltered except the move-out of the 310-loops shown by the red arrows. The superimposition of the N3A-N3A’ interfaces in the chimeric holoenzyme and the cAMP-bound RIα dimer (gray, PDB ID 4MX3) is shown in the dashed circle.