Figure 1.
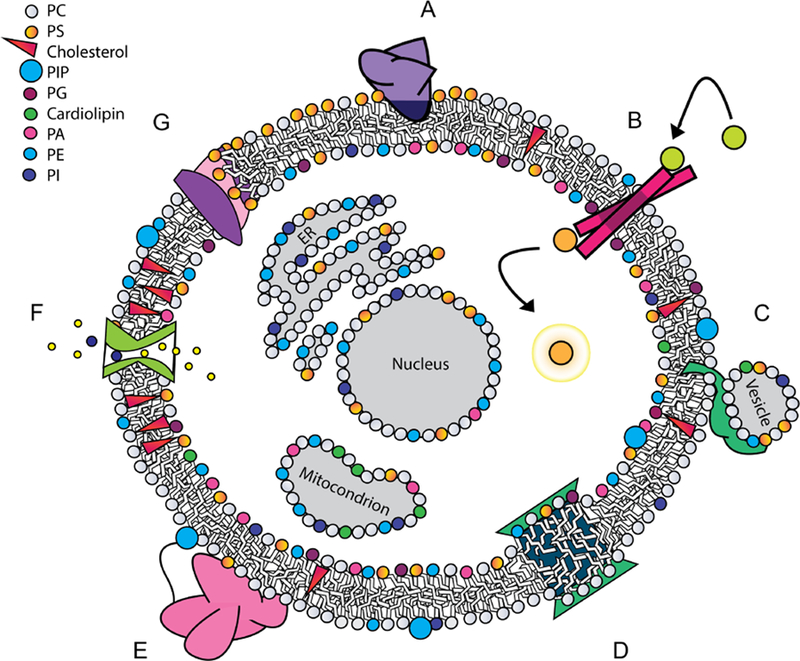
Proteins engage with lipids in diverse modes, many of which have functional significance. (A) Peripheral binding with a hydrophobic anchor, which can be lipid-specific, in this case to PS; (B) integral receptor involved in transmembrane signaling; (C) protein that induces vesicle fusion; (D) integral protein that induces local curvature through hydrophobic mismatch; (E) peripheral protein tethered to a membrane lipid, while its globular domain interacts with the interfacial region without embedding in the membrane core; (F) channel embedded in the membrane controlling ion transport across the membrane, while interacting with cholesterol; (G) transport of lipids across a membrane by a phospholipid scramblase.
