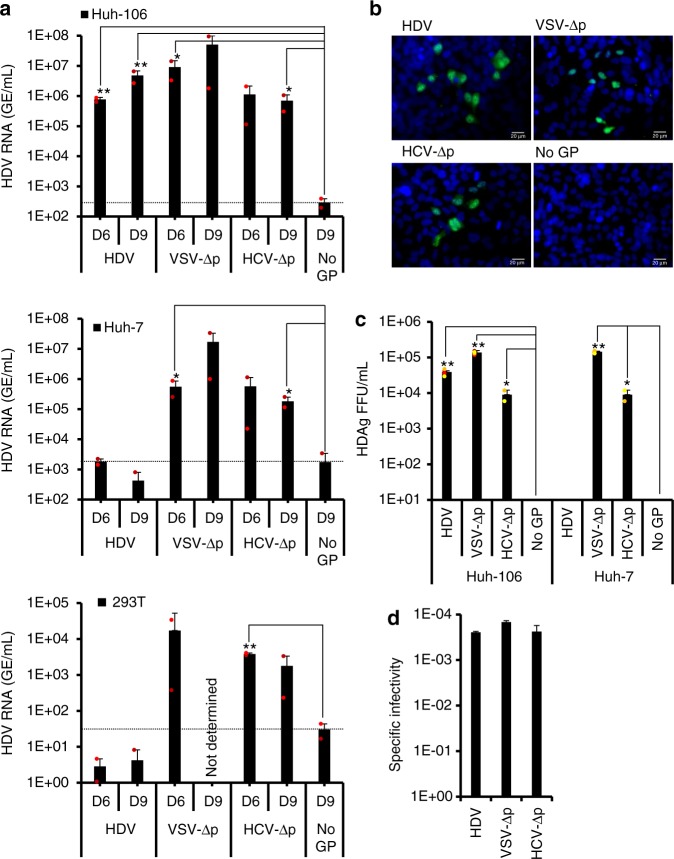
Fig. 2.
HDV particles generated with heterologous envelope glycoproteins are infectious. a The infectivity of virus particles produced with HBV (HDV), VSV (VSV-∆p), HCV (HCV-∆p) glycoproteins, or with no envelope glycoprotein (No GP) and harvested at day 6 or 9 post transfection (see Fig. 1a) was determined in Huh-106 (NTCP-expressing Huh-7 cells), Huh-7, or 293T cells, as indicated. Infected cells were grown for 7 days before total intracellular RNA was purified. The results of HDV RNA quantification by RT-qPCR are expressed as means (n = 2 independent experiments) per mL of cell lysates containing 105 cells. Nd, not determined. The dotted lines represent the experimental thresholds, as defined with the “No GP” controls. b, c Huh-106 and Huh-7 cells infected by serial dilutions of supernatants containing the indicated virus particles harvested at day 9 post transfection (Fig. 1a) were fixed at 7 days post infection and stained by immunofluorescence with the SE1679 polyclonal anti-HDAg antibody before counting the foci of HDAg-positive cell colonies. The cells were counterstained with Hoechst to visualize the nuclei. Scale bars represent 20 µm (b). The results from colony counting are expressed as means (n = 4 independent experiments) of FFU per mL of cell supernatants (c). d The specific infectivity values of the indicated viruses determined in Huh-106 infected cells were calculated from the experiments shown in c using the infectious titers and the HDV RNA contents of the inoculums. The results show the ratios of HDAg-positive FFU induced by HDV RNA from the same inoculums. Source data are provided as a Source Data file. Error bars correspond to standard deviation. Statistical analyses (Student’s t-test): p < 0.05 (*); p < 0.01 (**)