Figure 2.
Pola1 Is Expressed in Proliferating Progenitors During Embryonic and Postnatal Neurogenesis in the Mouse Brain, and POLA1-Mutated Cells Exhibit Variable POLα Expression
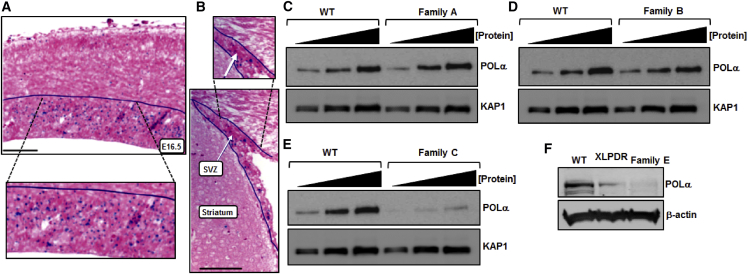
(A) The Pola1 transcript (dark blue signal) is found in the proliferative zone of the embryonic neocortex. The scale bar represents 200 μm. The dashed lines indicate an expanded area of the image.
(B) Three weeks after birth, Pola1 (dark blue signal) is expressed in the subventricular zone (SVZ), where postnatal neurogenesis occurs. The scale bar represents 200 μm. The dashed lines indicate an expanded area of the image.
(C) Increasing amounts of whole-cell extract (WCE) from LCLs derived from a clinically unaffected, unrelated, normal wild-type (WT) male individual and a POLA1-mutant-affected individual from family A were assessed for POLα expression levels. No difference in expression was observed.
(D) Increasing amounts of WCE from LCLs derived from the WT and a POLA1-mutant-affected individual from family B were assessed for POLα expression levels. POLα expression was comparable.
(E) Increasing amounts of WCE from LCLs derived from the WT and a POLA1-mutant-affected individual from family C were assessed for POLα expression levels. Here, POLα was markedly reduced in affected cells compared to in WT LCLs.
(F) POLα levels were assessed via WCE derived from dermal fibroblasts from the WT, an XLPDR-affected individual, and the POLA1-mutant-affected individual from family E. POLα was reduced in both instances of POLA1 mutation.