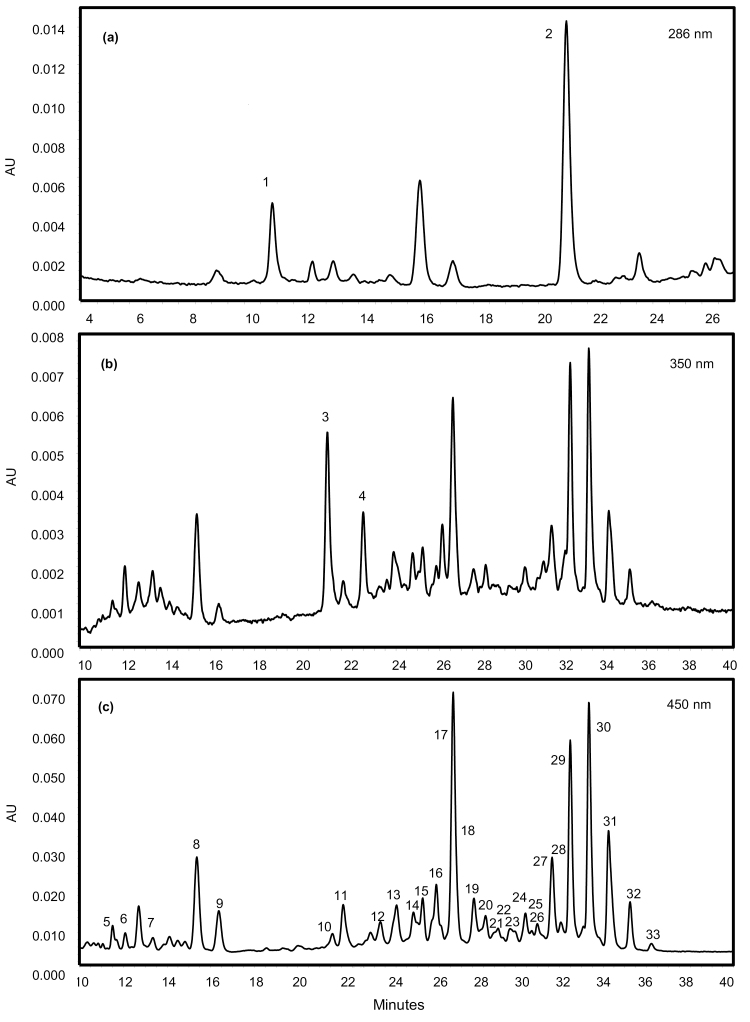
Fig. 2.
Typical HPLC-PDA profile of carotenoids and their esters in a red ripe chilli pepper (R1). HPLC-PDA analysis was performed in order to identify and quantify the carotenoids present in the ripe fruit of red chilli pepper (R1, high-intensity phenotype). Identification of esterified carotenoids and their corresponding fatty acids was carried out using LC-MS (Supplementary Table S2). Observation wavelengths (A) 286 nm, (B) 350 nm, and (C) 450 nm. Assignment of peaks: 1-α-tocopherol; 2-phytoene; 3-phytofluene-1; 4-phytofluene-2; 5-violaxanthin; 6-neoxanthin; 7-anther; 8-capsanthin; 9-zea; 10-anther mono; 11-β-cryptoxanthin; 12-anther mono; 13-anther mono; 14-caps mono (C12:0); 15-caps mono (C14:0); 16-anther mono; 17-β-carotene-1; 18-caps mono (C16:0); 19-β-carotene-2; 20-anther di; 21-capsorubin di (C12:0-C12:0); 22-capsorubin di (C12:0-C14:0); 23-zea di (C12:0-C14:0); 24-zea di (C14:0-C14:0); 25-zea di; 26-anther di; 27-caps di (C12:0-C12:0); 28-anther di; 29-caps di (C12:0-C14:0); 30-caps di (C14:0-C14:0); 31-caps di (C14:0-C16:0); 32-caps di (C16:0-C16:0); 33-zea di (C16:0-C16:0). Key: zea, zeaxanthin; anther, antheraxanthin; caps, capsanthin; mono, monoester; di, diester.