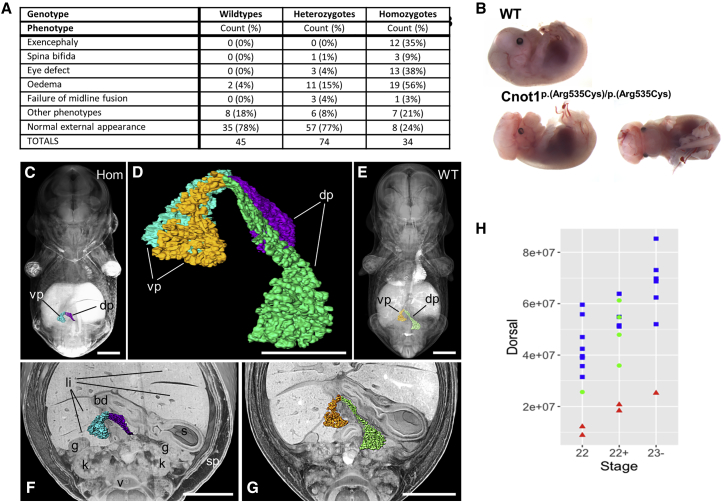
Figure 2.
Neurological and Pancreatic Abnormalities in Mouse Embryos Homozygous for the Cnot1 p.Arg535Cys Mutation
(A) Table listing the gross external phenotypes observed in E14.5 embryos. Numbers do not add to total as many embryos displayed multiple phenotypes. Significance by Fisher’s exact test, assuming an additive model. Exencephaly, p = 3.2 × 10−9; spina bifida, p = 0.027; eye defect, p = 5.5 × 10−8; edema, p = 2.6 × 10−7; midline defect, ns.
(B) Images showing representative E14.5 embryos: top shows wild-type embryo, bottom shows embryo homozygous for the CNOT1 p.Arg535Cys mutation with exencephaly and coloboma.
(C and E) Coronally sectioned, semi-transparent 3D volume models of stage-matched E14.5 embryos with superimposed models of the pancreas of homozygous (C) and wild-type (E) embryos.
(D) Overlay of extracted surface models of the pancreas of homozygous (blue, magenta) and wild-type embryos (orange, green).
(F and G) Coronally sectioned solid 3D volume rendered model of the abdomen of the embryos shown in (C) and (E) with superimposed pancreas. dp, dorsal pancreas; vp, ventral pancreas; li, liver lobes; s, stomach; sp, spleen; k, kidney; g, gonad; bd, bile duct.
Scale bars: 1,000 μm in (C), (E)–(G); 500 μm in (D).
(H) Graph showing the volume of the dorsal pancreas of E14.5 embryos in μm3. Blue squares show wild types, green circles are heterozygotes, and red triangles are homozygotes. Data analyzed using ANOVA with TukeyHSD posthoc test, effect of genotype p = 8.85 × 10−8; post hoc WT-Hom, p < 10−10; Het-Hom, p = 1.36 × 10−4, WT-Het, ns.