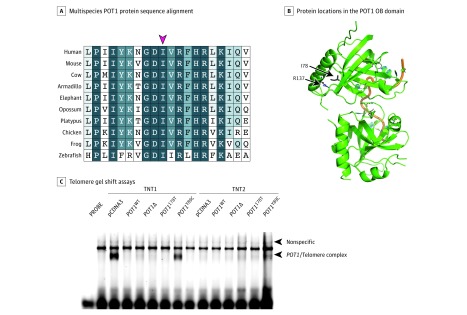
Figure 2. Functional Analyses of the Pathogenicity of the POT1 p.I78T Variant.
A, Multiple sequence alignment of the protection of telomeres 1 (POT1) protein sequence in humans and 9 other species. Shown are amino acid positions 69 to 88, relative to human POT1, with the red arrow indicating the highly conserved I78 residue. The best match in each protein alignment relative to human protein is shown. B, The location of the I78 residue on the structure of the POT1 oligonucleotide/oligosaccharide-binding fold (OB) domain is indicated, alongside another residue previously described as mutated in melanoma families (R137). Green ribbons represent the OB domains; orange thread, the telomere-like sequence. C, Telomere gel shift assays show that the POT1 p.I78T protein is unable to bind to a telomere-like sequence. Wild-type (WT) POT1, POT1 Y89C (a known pathogenic/disruptive variant) and POT1Δ (OB domain deletion) constructs were used as controls.5 TNT1 and TNT2 indicate separate in vitro translation reactions; pcDNA3 is an empty vector control. The arrow indicates the presence of a POT1 protein-telomere complex formed by the binding of in vitro translated POT1 protein to a telomere-like probe. Disruption of this protein-DNA complex is associated with telomere instability and a loss of telomere length control.