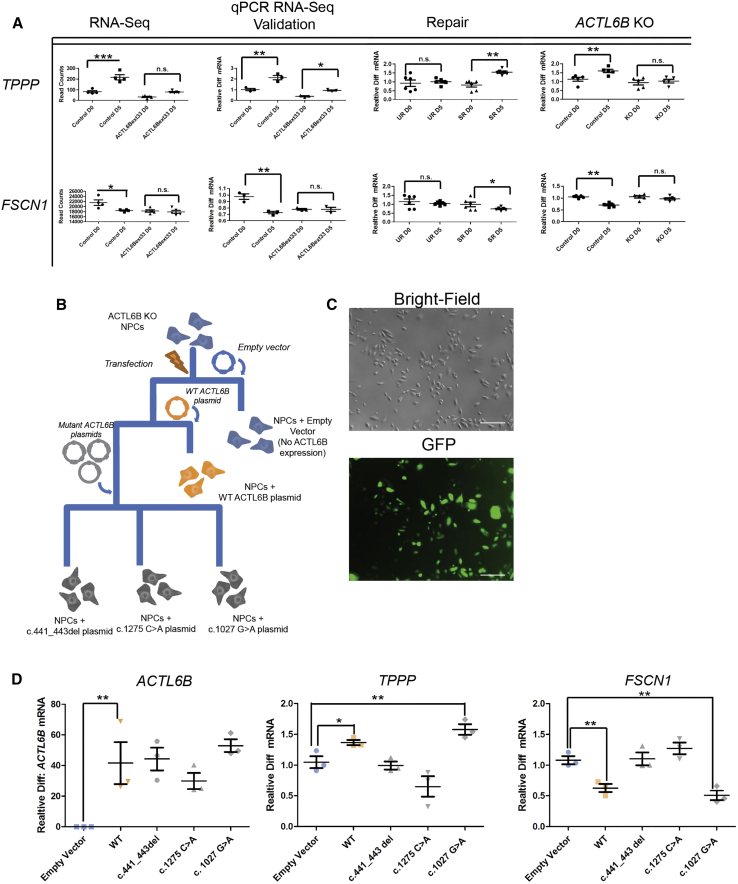
Figure 7.
External Validity in Multiple ACTL6B Mutant Models in Human Neurons
(A) TPPP and FSCN1 expression in initial RNA-seq (n ≥ 4) and qPCR (n ≥ 3) data (ACTL6Bext∗33 versus control); unrepaired (UR) ACTL6Bext∗33 versus ACTL6Bext∗33 successful repair (SR) (n = 6); and ACTL6B KO versus isogenic control cells (n = 5). Results are represented as mean ± SEM. Student’s t test, ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001.
(B) Experimental plan for generation of multiple human neuronal cell lines expressing various mutant ACTL6B constructs.
(C) Brightfield and GFP images demonstrating high transfection of ACTL6B constructs.
(D) mRNA expression in transfected ACTL6B KO NPCs at D5 time points of ACLT6B, TPPP, and FSCN1 (n = 3). Results are represented as mean ± SEM. Student’s t test, ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001.