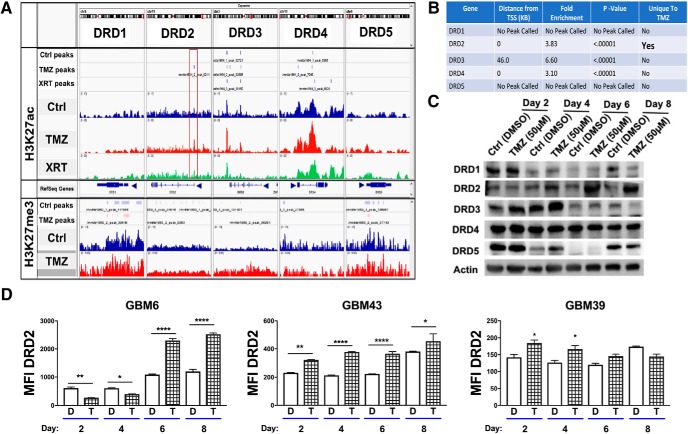
Figure 1.
Chemotherapeutic stress induces DRD2 expression in the patient-derived xenograft glioma lines. A, B, H3K27ac and H3K27me3 marks distribution around the transcription start sites of dopamine receptors following therapy. ChIP-Seq was performed for the open chromatin state H3K27 acetylation in PDX line GBM43 after 4 d of single exposure to TMZ (50 μm), or treated with one fractionated dose of radiotherapy (2 Gy). DMSO was used as a vehicle control. The red box in DRD2 highlights a key residue near the promoter that uniquely exhibited increased H3K27ac following TMZ treatment. (MACS2 peak score: 45.0, fold-enrichment: 4.023, p < 0.0001). Table summarizes statistical information for each of the five DRDs. Figure 1-1 also shows peak calling of all monoamine receptors. C, Western blot analysis of dopamine receptors expression in PDX cells treated with TMZ over 8 d. D, FACS analysis of DRD2 on different subtypes of PDX cells treated with vehicle control DMSO or TMZ (50 μm). Figure 1-2 includes analysis of all five DRDs demonstrating elevated DRD2 expression in human samples. Bars represent means from three independent experiments and error bars show the SD. Student t tests were performed for each day separately. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ****p < 0.0001.