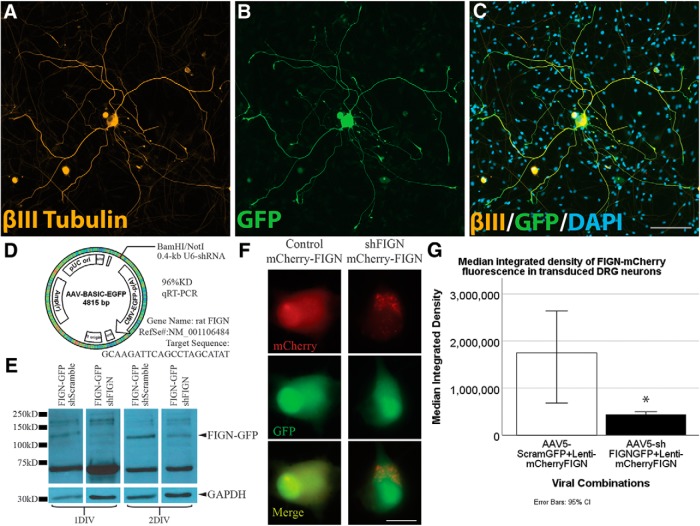
Figure 2.
AAV5–U6-shFIGN-CMV-GFP transduces neurons and knocks down fidgetin in vitro. Neurons were immunolabeled for the (A) neuron-specific tubulin, βIII-tubulin (yellow), (B) the AAV5 reporter protein GFP, and (C) DAPI (to counterstain nuclei). These images demonstrate the high ectopic expression of GFP in transduced adult DRG neurons after 8 DIV. The primary cell cultures were heterogeneous, as seen when comparing βIII-tubulin immunolabeling with the DAPI staining, as there are multiple cells that are not βIII-tubulin+. All neurons were GFP+ to some extent, but <10% of the non-neuronal cells were detectably GFP+. Scale bar, 100 μm. D, The AAV-ready plasmid was used to construct our AAV5, and the rat fidgetin gene was targeted with a sequence that demonstrated 96% knockdown of rat fidgetin via qRT-PCR. E, RFL-6 cells were conucleofected with the AAV5-U6-shFIGN-CMV-GFP or AAV5-U6-controlRNA-CMV-GFP and plasmid containing fidgetin-GFP fusion protein. A commercially available fidgetin antibody detects ectopically expressed fidgetin-GFP at a molecular weight of ∼130 kDa. This band disappears after 24 or 48 h of ectopic coexpression of shRNA and fidgetin-GFP. F, Live-cell imaging was used to detect ectopically expressed mCherry (top panels, red) and GFP (middle panels, green) in adult DRG neurons, and a reduction in mCherry fluorescence was observed with cotransduction using shFIGN AAV5. Scale bar, 20 μm. G, mCherry-fidgetin was ectopically expressed via a lentivirus cotransduced with the shFIGN or control AAV5s in adult DRG primary cultures. Neurons were identified in live-cell imaging, and the mean integrated density of mCherry fluorescence was significantly reduced when cotransduced with the shFIGN AAV5: *p < 0.001.