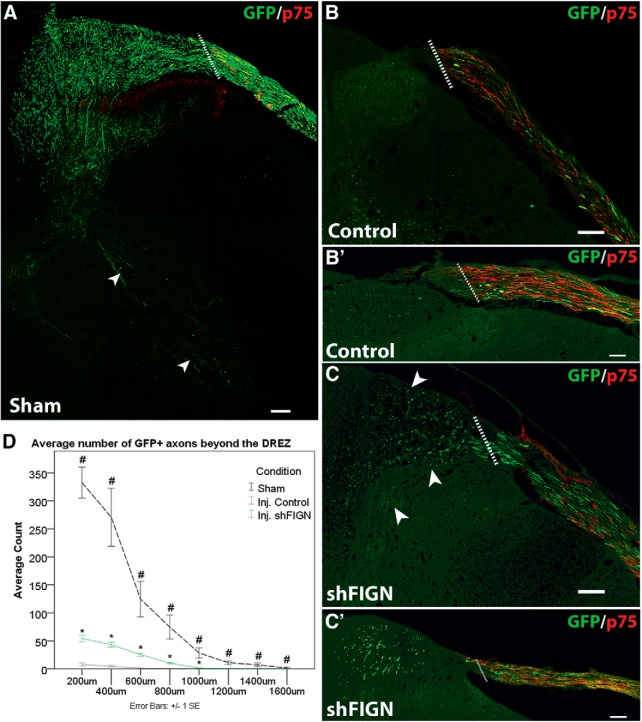
Figure 7.
Fidgetin knockdown promotes axonal regeneration beyond the DREZ following dorsal root crush injury. Anti-GFP and anti-p75 antibodies were used to visualize GFP+ axons and satellite glia, respectively. A, An uninjured sham animal injected with AAV5 displays robust GFP expression in axons within the dorsal root that traverse the DREZ and extend deep into the dorsal horn, with some axons extending into the ventral horn of the spinal cord (white arrows). B, B′, Following a dorsal root crush, axons rarely grow beyond the DREZ, demarcated by p75 immunolabeling. Dotted line indicates DREZ. C, C′, After fidgetin knockdown, axons can be seen crossing the DREZ and regenerating into the dorsal horn (arrows). Scale bars, 100 μm. D, The average number of GFP+ axons were quantified at 200 μm intervals beyond the DREZ for an uninjured control animal (n = 1 animal, 6 tissue sections), control AAV5 animals (n = 6 animals, 44 tissue sections), and shFIGN AAV5 animals (n = 6 animals, 50 tissue sections). Sections with an intact dorsal root and GFP+ axons were included in the analyses. Fidgetin knockdown significantly increased the amount of axonal regeneration beyond the DREZ and into the dorsal horn: *p < 0.05; #p < 0.05.