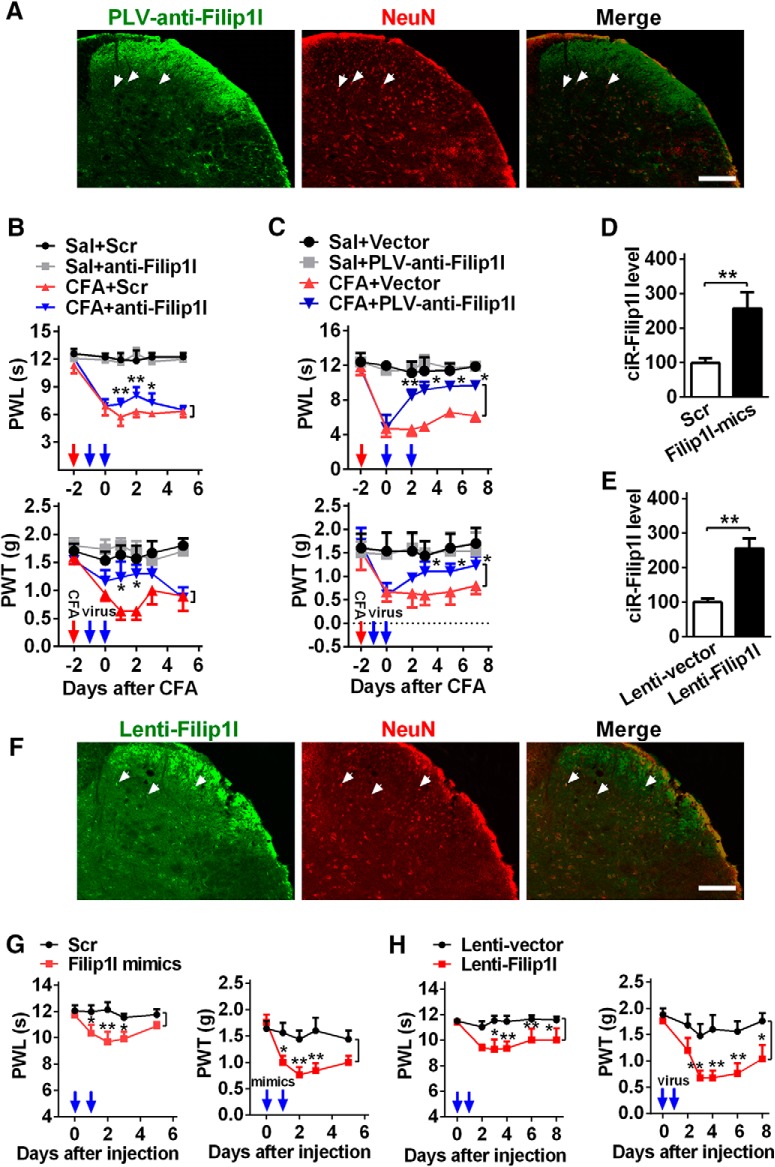
Figure 3.
circRNA-Filip1l contributes to nociceptive behavior. A, The infection of PLV-anti-Filip1l with GFP reporter in spinal cord of naive mice on day 3 after 2 consecutive days of intrathecal injection (day 5 after the first injection). NeuN, a neuron marker. Scale bar, 25 μm. B, C, Inhibition of circRNA-Filip1l alleviated the thermal hyperalgesia and mechanical allodynia after 2 consecutive days of intrathecal injections of anti-Filip1l (B) or PLV-anti-Filip1l (C) in CFA mice. n = 6 per group. Two-way ANOVA (effect vs group × time interaction) followed by post hoc Tukey test: *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01. Red arrow indicates CFA or saline injections. Blue arrows indicate anti-Filip1l or scrambled (Scr) and PLV-anti-Filip1l or vector injections. The anti-Filip1l sequence was antisense strand of full-length of circRNA beginning from junction. D, E, Intrathecal injections of circRNA-Filip1l mimics (D) or Lenti-Filip1l (E) for 2 consecutive days increased the spinal circRNA-Filip1l content in naive mice. n = 5 per group. Two-tailed paired Student's t test: **p < 0.01. F, The infection of Lenti-Filip1l with GFP reporter in spinal cord of naive mice on day 3 after 2 consecutive days of intrathecal injection. Scale bar, 25 μm. G, H, Overexpression of circRNA-Filip1l induced the generation of pain-like behavior after 2 consecutive days of intrathecal injections of circRNA-Filip1l mimics (G) or Lenti-Filip1l (H). n = 6 per group. Two-way ANOVA (effect vs group × time interaction) followed by post hoc Tukey test: *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01. Blue arrows indicate circRNA-Filip1l mimics or Scr and Lenti-Filip1l or Lenti-vector injections.