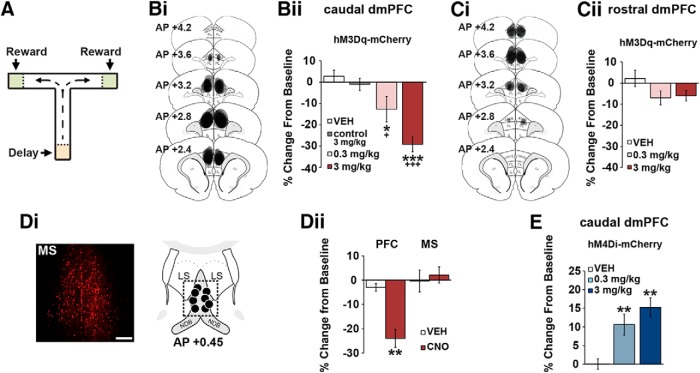
Figure 2.
CRF neurons in the caudal, but not rostral, dmPFC modulate working memory. A, T-maze schematic. Bi, Schematics depict hM3Dq viral spread in the caudal dmPFC (anteroposterior 3.2–2.2) from all animals tested. Bii, CNO dose-dependently impairs task performance relative to vehicle (n = 7) and CNO-treated viral control animals (n = 7; control 3 mg/kg). Ci, hM3Dq viral spread in the rostral dmPFC (anteroposterior 4.2–3.2). Cii, Chemogenetic activation of CRF neurons in the rostral dmPFC has no significant effects on task performance relative to vehicle (n = 6) and viral controls (n = 7). Di, Left, Retrograde mCherry cell body labeling observed in the MS in ∼30% of animals. Right, Schematics representing intra-MS infusion sites (n = 4). Dii, When infused into the PFC, 0.5 mm CNO robustly impairs task performance (n = 7), while having no effects on performance when infused into the MS (n = 4). E, Chemogenetic suppression of CRF neurons in the caudal dmPFC improves task performance relative to vehicle (n = 8) and CNO-treated viral controls (n = 7). Results are mean ± SEM percentage change in accuracy relative to baseline. *p < 0.05 versus vehicle. +p < 0.001 versus viral controls. **p < 0.01 versus vehicle. ***p < 0.001 versus vehicle. +++p < 0.001 versus viral controls.